In Forex trading, economic data plays a crucial role in shaping market sentiment and driving price movements. Among the most influential economic indicators is NFP (non-farm payroll), a key employment report that provides insights into the strength of the U.S. labor market.
Released monthly by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the NFP report measures job creation across various industries, excluding farm workers, private household employees, and government agency workers. Traders and investors closely monitor employment data because it directly impacts central bank policies, particularly those of the Federal Reserve.
This article explores the role of employment data in Forex analysis, with a particular focus on non farm payroll, the unemployment rate, and wage growth. By understanding how these indicators affect market movements, traders can make informed decisions and incorporate employment data into their fundamental analysis strategy.
Understanding Employment Data in Forex Analysis
Employment data is one of the most critical fundamental indicators in Forex trading, as it reflects the overall health of an economy. Among the various employment reports, the non farm payroll (NFP) report stands out as a major market mover, often triggering significant volatility in currency pairs, especially those involving the U.S. dollar. However, employment data goes beyond just non farm payroll figures—it also includes the unemployment rate and wage growth, both of which influence central bank decisions and market sentiment.
How Employment Data Reflects Economic Strength
Employment levels serve as a direct measure of economic growth. A rising non farm payroll figure suggests that businesses are hiring more workers, indicating economic expansion. More jobs typically lead to higher consumer spending, which fuels economic growth and inflation.
On the other hand, declining job numbers or increasing unemployment rates signal potential economic weakness, prompting concerns about lower consumer spending and a possible economic slowdown.
Employment Data and Its Relationship with Central Banks
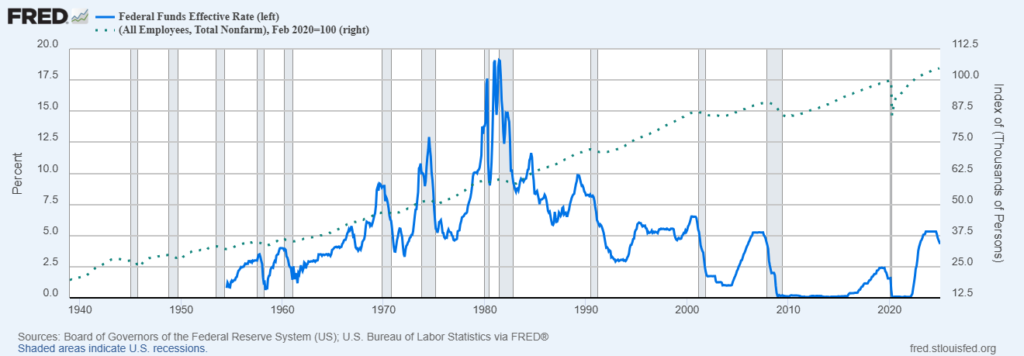
Central banks, particularly the Federal Reserve, closely monitor employment data when setting monetary policy. The Fed operates under a dual mandate: maintaining price stability (inflation control) and achieving maximum employment.
A strong non farm payroll report, coupled with low unemployment and rising wages, often leads to tighter monetary policy (interest rate hikes) to prevent inflation from overheating.
Conversely, weak employment data may push central banks to lower interest rates or implement stimulus measures to support job growth and economic activity.
Why Forex Traders Monitor Employment Data
Forex traders pay close attention to employment reports because they influence market expectations regarding interest rates. Since higher interest rates generally strengthen a currency by attracting foreign investment, positive non farm payroll results tend to boost the U.S. dollar.
In contrast, weaker employment data can lead to dollar weakness as traders anticipate lower interest rates. Understanding these dynamics allows traders to position themselves ahead of major employment data releases and capitalize on market movements.
Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) and Its Impact on Forex
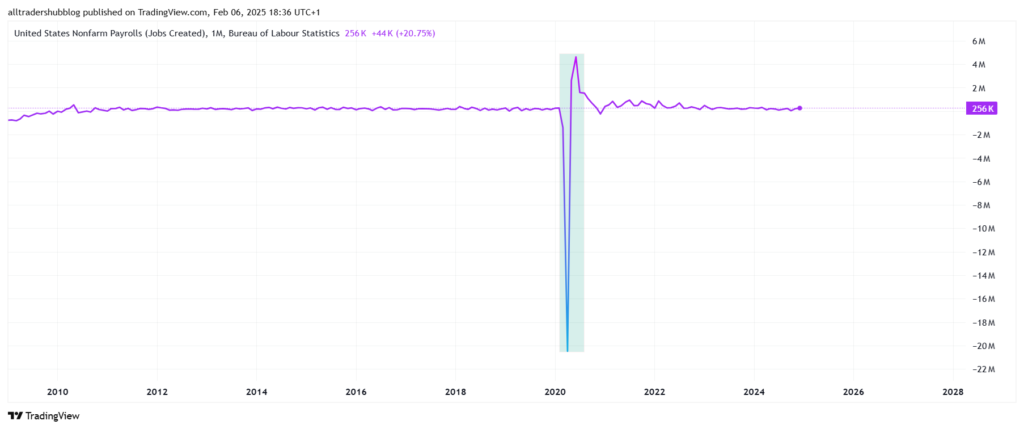
The non farm payroll (NFP) report is one of the most closely watched economic indicators in Forex trading. Released on the first Friday of each month by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the non farm payroll report measures the total number of jobs added or lost in the U.S. economy, excluding farm workers, private household employees, and government agency workers. Because employment is a key driver of economic growth, the NFP report provides valuable insights into the health of the U.S. economy and directly impacts the U.S. dollar (USD).
How NFP Affects Forex Markets
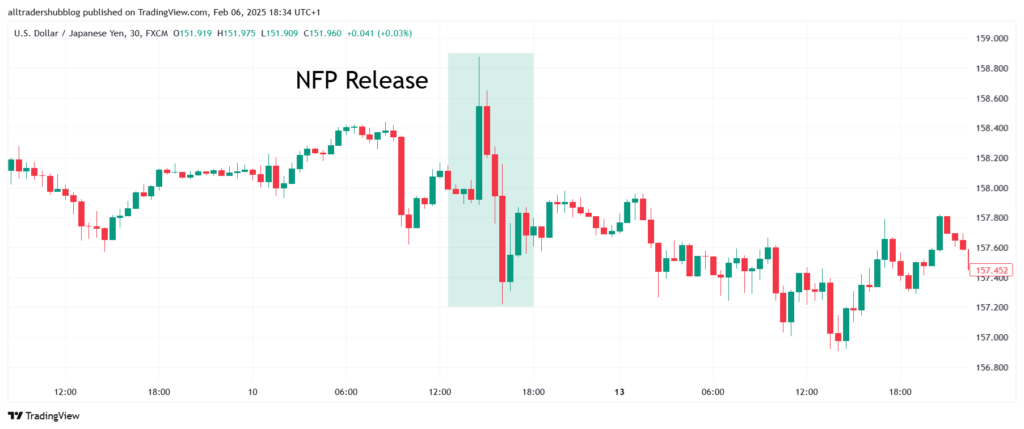
The non farm payroll report often causes sharp volatility in currency markets, particularly in USD pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY. This is because the report influences market expectations regarding Federal Reserve policy.
- Stronger-than-expected NFP data – If the number of jobs added exceeds market expectations, it suggests a strong labor market, increasing the likelihood of interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve. Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, strengthening the U.S. dollar.
- Weaker-than-expected NFP data – If the report shows fewer jobs added or job losses, it signals economic weakness. Traders may anticipate lower interest rates or stimulus measures, leading to USD depreciation.
Market Expectations vs. Actual Results
One of the key factors in how the non farm payroll report affects Forex markets is the difference between actual job numbers and market expectations. Traders and institutional investors often position themselves based on forecasts from economists. If the NFP data significantly deviates from expectations, it can lead to large price swings as traders adjust their positions.
For example:
- If the forecast for non farm payroll is 200K jobs but the actual number is 300K, the USD may rally as traders anticipate a more aggressive Fed policy.
- If the forecast is 200K but the actual number is only 100K, the USD may weaken due to fears of economic slowdown.
Case Studies: NFP’s Impact on Major Currency Pairs
- EUR/USD Reaction to NFP (June 2023) – A higher-than-expected non farm payroll figure of 339K (vs. 190K expected) caused the USD to strengthen, leading to a sharp drop in EUR/USD.
- USD/JPY Volatility (September 2022) – A weaker-than-expected NFP print of 263K (vs. 315K expected) resulted in a temporary drop in USD/JPY, as traders anticipated a softer Fed stance.
Trading Strategies for NFP Releases
Because of the volatility surrounding the non farm payroll report, traders often use specific strategies to capitalize on price movements:
- Breakout Trading – Traders wait for the initial NFP spike and enter trades based on strong momentum in the direction of the breakout.
- Pullback Strategy – After the initial reaction, traders wait for a retracement before entering a trade in the direction of the dominant move.
- Straddle Strategy – Placing buy and sell stop orders above and below the current price before the NFP release to capture movement in either direction.
Unemployment Rate and Its Role in Forex Trading
The unemployment rate is a key economic indicator that provides insights into the health of a country’s labor market. In Forex trading, it plays a crucial role in shaping currency movements, as it directly influences central bank policies and investor sentiment. While the non farm payroll report gives a snapshot of job creation, the unemployment rate measures the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed and actively seeking work. Traders analyze this data alongside non farm payroll figures to assess the broader economic outlook and make informed trading decisions.
How the Unemployment Rate Affects Forex Markets
The unemployment rate is a lagging economic indicator, meaning it reflects past economic conditions rather than predicting future trends. However, its impact on Forex markets is significant because of its strong correlation with monetary policy.
- Lower Unemployment Rate – A declining unemployment rate suggests a strong labor market and economic expansion. If the rate drops alongside strong non farm payroll figures, traders may anticipate tighter monetary policy (interest rate hikes) from the central bank, leading to currency appreciation.
- Higher Unemployment Rate – A rising unemployment rate signals economic weakness, reducing consumer spending and business investment. If unemployment increases, central banks may respond with lower interest rates or stimulus measures, leading to currency depreciation.
For example, if the U.S. unemployment rate drops from 4.0% to 3.5%, the market may expect the Federal Reserve to maintain or raise interest rates, strengthening the U.S. dollar. Conversely, a rise in unemployment to 5.0% may increase expectations of rate cuts, weakening the USD.
Unemployment Rate and Central Bank Policies
Central banks, particularly the Federal Reserve, closely monitor the unemployment rate as part of their decision-making process. The Fed’s dual mandate focuses on:
- Price Stability (Inflation Control) – Managing inflation to prevent excessive price increases.
- Maximum Employment – Ensuring a strong labor market with low unemployment.
If unemployment rises sharply, the Fed may prioritize economic growth over inflation control, leading to interest rate cuts. Conversely, if the unemployment rate is exceptionally low, the Fed may worry about wage inflation and consider raising rates.
Historical Examples of Unemployment Rate Impact on Forex Markets
- COVID-19 Pandemic (2020) – The U.S. unemployment rate skyrocketed from 3.5% to 14.8% in April 2020, leading to aggressive Federal Reserve rate cuts and quantitative easing. As a result, the U.S. dollar weakened significantly against major currencies.
- U.S. Labor Market Recovery (2021-2022) – As the unemployment rate steadily declined, the Fed shifted towards tightening monetary policy, boosting the U.S. dollar against currencies like the euro and yen.
Trading Strategies Based on the Unemployment Rate
Forex traders incorporate the unemployment rate into their fundamental analysis, often using it in conjunction with non farm payroll data to predict currency movements. Some common strategies include:
- Fundamental Bias Trading – If the unemployment rate is declining and non farm payroll data is strong, traders may take long positions on the currency, anticipating central bank hawkishness.
- Interest Rate Expectations – Traders monitor unemployment trends to forecast interest rate decisions and adjust their positions accordingly.
- Correlation with Other Economic Indicators – Combining the unemployment rate with wage growth and inflation data to build a complete macroeconomic picture.
Wage Growth and Its Influence on Currency Markets
Wage growth is a critical component of employment data that significantly impacts Forex markets. While the non farm payroll report reveals how many jobs were added or lost, wage growth provides insights into the quality of those jobs and their impact on inflation. Rising wages typically indicate a strong labor market and increased consumer spending, which can drive economic growth and influence central bank policies. Forex traders closely monitor wage growth data because it affects interest rate expectations and, ultimately, currency valuations.
Why Wage Growth Matters in Forex Trading
Wage growth reflects how much employees are earning on average, and its implications go beyond just the labor market:
- Inflationary Pressure – When wages rise, workers have more disposable income, leading to increased consumer spending. Higher demand for goods and services can push inflation higher, which central banks may counter by raising interest rates.
- Central Bank Policy Decisions – Central banks like the Federal Reserve consider wage growth when setting interest rates. If wages are rising too fast, the Fed may implement rate hikes to prevent the economy from overheating, which often strengthens the U.S. dollar.
- Real vs. Nominal Wage Growth – Traders differentiate between nominal wage growth (before inflation) and real wage growth (adjusted for inflation). If wages are rising but inflation is outpacing them, consumers may still struggle, leading to weaker economic growth.
Wage Growth and Its Relationship with Non Farm Payroll Data
Although the non farm payroll report focuses on job creation, the accompanying wage growth figures can sometimes have an even greater impact on Forex markets. Here’s why:
- Strong NFP but Weak Wage Growth – If the economy adds a high number of jobs but wage growth remains stagnant, it suggests that new jobs are lower-paying or that inflationary pressures remain low. This scenario may reduce expectations of aggressive central bank rate hikes, weakening the currency.
- Moderate NFP with Strong Wage Growth – If job creation is in line with expectations but wages are rising faster than forecasted, it signals increasing inflationary pressure. The central bank may respond with tighter monetary policy, strengthening the currency.
For example, if the non farm payroll report shows 250K new jobs but wage growth comes in lower than expected at 0.1% month-over-month, the U.S. dollar may weaken as traders anticipate a less hawkish Fed. On the other hand, if wage growth surprises to the upside at 0.5%, the dollar could rally due to higher inflation expectations.
Case Studies: Wage Growth’s Impact on Forex Markets
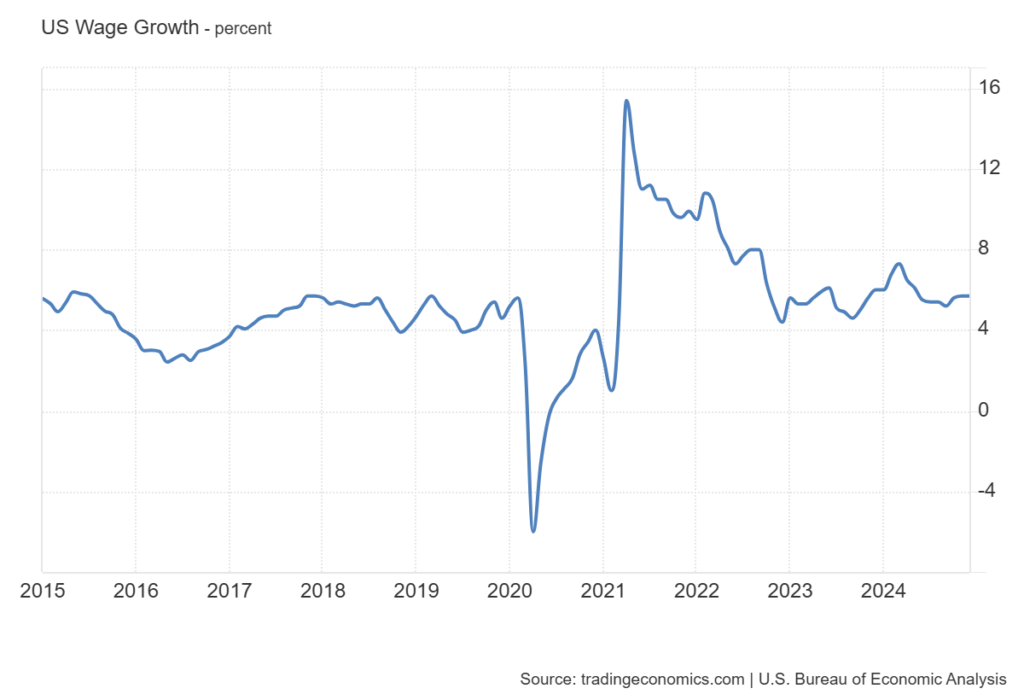
- U.S. Wage Growth and the Fed’s Tightening Cycle (2018) – As U.S. wage growth accelerated, the Federal Reserve responded with multiple rate hikes, boosting the dollar against major currencies.
- Wage Growth Slowdown Post-COVID (2021-2022) – Despite strong non farm payroll numbers, sluggish wage growth led to speculation that inflationary pressures were easing, causing temporary USD weakness.
How Forex Traders Use Wage Growth Data
To incorporate wage growth into Forex analysis, traders:
- Monitor Monthly Earnings Reports – Pay close attention to the “Average Hourly Earnings” data released alongside non farm payroll figures.
- Compare Wage Growth with Inflation – Analyze whether rising wages are outpacing inflation or if real incomes are declining.
- Use Wage Growth as a Leading Indicator – Strong wage growth often leads to higher inflation, which can signal future interest rate hikes and currency appreciation.
How to Trade Forex Using Employment Data
Employment data is one of the most influential fundamental drivers in Forex trading. Reports like non farm payroll, the unemployment rate, and wage growth provide valuable insights into economic strength and central bank policy expectations. Traders use this data to anticipate market trends, identify potential trade setups, and manage risk effectively.
Key Steps to Trading Forex with Employment Data
1. Monitor Economic Calendar for Employment Reports
The first step in trading employment data is to stay informed about scheduled releases. The most important employment-related reports include:
- Non Farm Payroll (NFP) – Released on the first Friday of every month by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, it measures job creation in the non-agricultural sector.
- Unemployment Rate – Published alongside NFP, it reflects the percentage of the workforce that is unemployed and actively seeking work.
- Wage Growth (Average Hourly Earnings) – Measures the change in earnings over time, indicating potential inflationary pressures.
Checking an economic calendar allows traders to prepare for potential volatility around these key releases.
2. Understand Market Expectations vs. Actual Data
Forex markets react not only to employment figures but also to how they compare with market forecasts. Before the release, analysts and economists provide estimates for NFP, the unemployment rate, and wage growth. The actual data is then compared to these expectations:
- Better-than-expected data – A higher non farm payroll number, lower unemployment rate, or stronger wage growth often leads to a stronger U.S. dollar, as traders anticipate higher interest rates.
- Worse-than-expected data – A disappointing NFP print, rising unemployment, or weak wage growth may cause USD weakness, as markets price in potential rate cuts or economic slowdown.
- Mixed data – If NFP exceeds expectations but wage growth disappoints, or unemployment rises despite strong job creation, price action may be more uncertain.
3. Trading Strategies for Employment Data Releases
Since employment reports can create high volatility, traders use specific strategies to capitalize on price movements while managing risk.
A. Breakout Strategy
The breakout strategy is designed to capture large price moves immediately after the data release. Traders place buy and sell stop orders above and below key levels, allowing them to enter a trade in the direction of the breakout.
Steps:
- Identify key support and resistance levels before the report.
- Place pending buy and sell stop orders just beyond these levels.
- Let the market determine the trade direction after the data release.
- Use a stop-loss to protect against whipsaws.
B. Pullback Strategy
For traders who prefer to avoid initial volatility, the pullback strategy involves waiting for the market’s reaction and entering on a retracement.
Steps:
- Observe the initial spike after the NFP release.
- Wait for the price to pull back to a key technical level (e.g., a previous support/resistance or Fibonacci retracement).
- Enter in the direction of the dominant trend once price stabilizes.
- Use a stop-loss to control risk.
C. Trend-Following Strategy Based on Employment Trends
Instead of trading short-term spikes, some traders analyze long-term employment trends and position themselves accordingly.
Steps:
- Monitor multi-month trends in non farm payroll, unemployment, and wage growth.
- Identify the impact on central bank policy—strong employment data may lead to a hawkish stance, boosting the currency.
- Use technical confirmation (e.g., moving averages, trendlines) to time entries.
4. Managing Risk When Trading Employment Data
Trading employment data can be highly profitable but also risky due to increased volatility. Risk management techniques include:
- Using Stop-Loss Orders – To prevent large losses in case of unexpected price swings.
- Avoiding Overleveraging – Employment reports can cause major price movements, so using excessive leverage can lead to account blowouts.
- Waiting for Market Reaction – Instead of jumping in immediately after the release, waiting a few minutes can help avoid whipsaws.
Employment Data and Central Bank Policies
Employment data is one of the most important factors influencing central bank policies. Reports like non farm payroll, the unemployment rate, and wage growth provide central banks with a clearer picture of economic health, helping policymakers determine whether to raise, lower, or maintain interest rates. Since monetary policy decisions directly impact currency valuations, Forex traders closely analyze employment data to anticipate potential shifts in central bank policy.
How Central Banks Use Employment Data
Most central banks, including the U.S. Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank (ECB), and the Bank of England (BoE), have dual or primary mandates that focus on:
- Price Stability (Inflation Control) – Ensuring inflation remains within a target range (typically around 2%).
- Employment Growth (Maximum Employment) – Supporting a strong labor market with low unemployment.
Employment data, especially non farm payroll reports and wage growth figures, plays a crucial role in shaping a central bank’s stance on monetary policy.
- Strong Employment Data → Tighter Monetary Policy (Rate Hikes)
If job creation is high, the unemployment rate is low, and wage growth is strong, central banks may see the economy as overheating. To prevent excessive inflation, they might raise interest rates, which strengthens the currency.- Example: A higher-than-expected non farm payroll print and rising wages may lead the Federal Reserve to hike rates, boosting the U.S. dollar.
- Weak Employment Data → Looser Monetary Policy (Rate Cuts)
If job growth slows, unemployment rises, and wages stagnate, central banks may adopt a more accommodative policy by lowering interest rates or implementing quantitative easing (QE). Lower rates reduce the currency’s attractiveness to investors, leading to depreciation.- Example: A disappointing NFP report with weak wage growth may increase expectations of a Fed rate cut, weakening the U.S. dollar.
Employment Data’s Role in Forward Guidance
Central banks use forward guidance to communicate their expectations for future monetary policy. Employment data plays a critical role in shaping these statements.
- Hawkish Forward Guidance – If employment remains strong, central banks may signal future rate hikes, strengthening the currency.
- Dovish Forward Guidance – If employment weakens, central banks may hint at future rate cuts or stimulus measures, leading to currency depreciation.
For instance, when Federal Reserve officials discuss the labor market in their speeches, Forex traders analyze their tone (hawkish or dovish) to adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
Case Studies: Employment Data and Central Bank Reactions
- Federal Reserve Rate Hikes (2015-2018) – As U.S. employment data consistently improved, with strong non farm payroll numbers and wage growth, the Fed embarked on a series of rate hikes. This strengthened the U.S. dollar against major currencies.
- COVID-19 Response (2020) – The sharp rise in unemployment due to lockdowns forced the Fed to cut rates to near zero and introduce QE, leading to a weaker dollar.
- Post-Pandemic Recovery (2021-2023) – As employment rebounded, the Fed shifted to a more hawkish stance, hiking rates to combat inflation, strengthening the USD.
Trading Forex Based on Employment Data and Central Bank Policy
To trade Forex effectively using employment data and central bank policy expectations, traders should:
- Analyze the relationship between employment data and inflation – If job growth is strong but inflation remains stable, the central bank may not rush to raise rates.
- Monitor central bank statements – Speeches from policymakers provide insights into how they interpret employment data.
- Follow market expectations for rate decisions – Interest rate futures and bond yields can help traders gauge how employment data is influencing rate hike/cut expectations.
Conclusion
Employment data is one of the most powerful fundamental indicators in Forex analysis, directly influencing currency movements and central bank policies. Reports such as non farm payroll, the unemployment rate, and wage growth provide traders with valuable insights into the strength of an economy and the potential direction of monetary policy.
A strong labor market, characterized by robust job creation and rising wages, often leads to tighter monetary policy, strengthening a country’s currency. Conversely, weak employment data can signal economic slowdown, prompting central banks to lower interest rates, which typically weakens the currency. Understanding these relationships allows traders to anticipate market reactions and make informed trading decisions.
To effectively trade Forex using employment data, traders must:
- Monitor economic calendars and prepare for high-impact employment reports.
- Compare actual employment figures with market expectations to gauge currency reactions.
- Align employment data with central bank policy expectations to refine trading strategies.
- Manage risk carefully, as employment reports, especially NFP, can cause significant volatility.
By mastering the role of employment data in Forex trading, traders can improve their ability to navigate market movements, capitalize on economic trends, and develop a well-rounded approach to fundamental analysis.
