Central bank policies are one of the most powerful forces shaping currency values. Institutions like the U.S. Federal Reserve (Fed), the European Central Bank (ECB), and the Bank of Japan (BoJ) have a massive influence on their economies through the monetary policies they implement. While many traders zero in on technical analysis, understanding what central banks are doing—and why—is a must for anyone using fundamental analysis in forex trading.
Central banks have a range of tools at their disposal to manage economic conditions, but two of the most impactful are interest rates and quantitative easing. These tools are designed to tackle goals like controlling inflation, stabilizing the currency, and encouraging economic growth. However, the actions central banks take often cause ripples in the forex markets, making it vital for traders to stay on top of these developments.
Knowing how central banks operate and being able to predict their policy decisions can give forex traders a significant edge. Those who can interpret these moves accurately and adjust their strategies accordingly are better positioned to profit from market fluctuations.
In this article, we’ll break down the key aspects of central bank policies and their influence on currency markets. We’ll also look at actionable trading strategies and discuss some of the common hurdles traders face when analyzing these policies. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your approach, understanding the role of central banks can give you a clearer perspective on market movements.
The Role of Central Banks in the Forex Market
Central banks are among the most powerful entities in the financial world. They are serving as the primary monetary authorities in their respective countries. Their actions, whether planned or unexpected, can create significant ripples in the forex market. Thus, affecting currency values and overall market sentiment.
Understanding the role of central banks is fundamental for forex traders. These institutions are key players in shaping economic conditions and influencing exchange rates.
Overview of Central Banks
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (Fed), the European Central Bank (ECB), and the Bank of Japan (BoJ), have a clear mandate to manage their country’s monetary policy. Their primary goals typically include:
- Controlling Inflation: Central banks aim to keep inflation within a specific target range (often around 2%). High inflation erodes purchasing power and can destabilize an economy. Central banks use tools like interest rate adjustments to curb rising prices.
- Stabilizing the Currency: By managing inflation and economic growth, central banks help maintain the stability of their national currency. Currency stability is crucial for trade and investment, as significant fluctuations can disrupt economic activities.
- Promoting Economic Growth and Employment: Many central banks, like the U.S. Federal Reserve, have a dual mandate to maximize employment while keeping inflation in check. This involves adjusting monetary policy to support job creation and sustainable economic growth.
These core objectives drive central bank decisions and have a direct impact on the forex market. Therefore, making it essential for traders to pay close attention to their policies and actions.
Key Tools Used by Central Banks
Central banks employ a variety of tools to achieve their objectives, but the most influential ones affecting forex markets include:
Interest Rate Adjustments
Interest rates are perhaps the most well-known tool in a central bank’s arsenal. By raising or lowering the benchmark interest rate, central banks can influence economic activity:
- Raising Interest Rates: When a central bank increases interest rates, it typically signals efforts to curb inflation. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive and saving more attractive, which can slow down economic growth. However, higher rates often lead to currency appreciation because foreign investors seek higher returns, increasing demand for that currency.
- Lowering Interest Rates: Conversely, lowering interest rates is a move to stimulate economic activity. Cheaper borrowing costs can encourage businesses to invest and consumers to spend, potentially boosting economic growth. However, lower interest rates can weaken a currency, as investors look for higher-yielding assets elsewhere.
For example, when the Fed hikes interest rates, it often leads to a stronger U.S. dollar (USD). As the investors anticipate higher returns on U.S. assets. This increase in demand for USD can affect currency pairs like EUR/USD or GBP/USD.
Quantitative Easing (QE)
Quantitative Easing (QE) is a non-traditional monetary policy tool used by central banks to increase the money supply and stimulate economic growth, particularly during times of financial crisis or economic stagnation. QE involves the central bank purchasing long-term securities, such as government bonds, to inject liquidity into the financial system.
- Impact on Currency Values: QE typically leads to currency depreciation because it increases the money supply, reducing the currency’s value. For instance, when the ECB implemented QE during the Eurozone debt crisis, the euro weakened against other major currencies like the U.S. dollar.
- Signaling Effect: The announcement or anticipation of QE can have a significant impact on forex markets. Even before the actual implementation, the expectation of increased money supply can cause a currency to weaken as traders price in the effects.
Forward Guidance
Forward guidance is a communication strategy used by central banks to influence market expectations about future policy actions. By providing indications about the likely path of interest rates or other policy measures, central banks aim to shape investor behavior and market sentiment.
- Market Impact: If a central bank signals that it plans to raise interest rates in the near future, traders may start buying the currency in anticipation of higher yields. Conversely, dovish forward guidance, suggesting rate cuts or continued monetary easing, can lead to currency depreciation.
For instance, when the BoE provided hawkish forward guidance signaling potential rate hikes, the British pound (GBP) often appreciated against other currencies like the euro (EUR) or Japanese yen (JPY).
The Central Bank’s Influence on Market Sentiment
Central banks have a profound impact on market sentiment. The decisions they make and the language they use can lead to swift and sometimes volatile reactions in the forex market. Traders closely monitor central bank meetings, press conferences, and economic reports to gauge the potential direction of monetary policy. Even subtle changes in a central bank’s tone—from dovish (favoring loose monetary policy) to hawkish (favoring tight monetary policy)—can trigger significant moves in currency pairs.
For example:
- Hawkish Signals: When a central bank signals tighter monetary policy, such as an interest rate hike, traders often interpret this as a sign of economic strength. This typically leads to an increase in demand for the currency, causing it to appreciate.
- Dovish Signals: On the other hand, dovish signals suggesting potential rate cuts can indicate economic weakness, leading to a decrease in demand for the currency and causing it to depreciate.
By keeping a close watch on central bank activities, traders can anticipate potential market movements and make more informed trading decisions.
Understanding Interest Rates and Their Impact on Forex
Interest rates are one of the most powerful tools used by central banks to influence economic activity, and their adjustments can have profound effects on the forex market. For traders, understanding how interest rates impact currency values is essential for making informed decisions and developing successful trading strategies.
What Are Interest Rates?
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money. When you take out a loan, the interest rate is the percentage you pay to the lender on top of the principal amount. For central banks, the interest rate typically refers to the benchmark or policy rate, such as the Federal Funds Rate set by the U.S. Federal Reserve or the ECB’s refinancing rate. These benchmark rates influence the interest rates that banks charge each other for overnight loans and affect borrowing costs throughout the economy.
Central banks adjust interest rates to either stimulate or cool down economic activity:
- Rate Hikes: Raising interest rates makes borrowing more expensive and saving more attractive. This helps slow down inflation by reducing consumer spending and business investment.
- Rate Cuts: Lowering interest rates reduces the cost of borrowing, encouraging businesses to invest and consumers to spend. This stimulates economic growth but can also lead to higher inflation if the economy overheats.
How Interest Rate Changes Affect Currency Values
Interest rates have a direct impact on currency values because they influence the flow of capital between countries. Generally, higher interest rates attract foreign investors looking for better returns, increasing demand for the currency. Conversely, lower interest rates tend to weaken a currency as investors seek higher yields elsewhere.
Interest Rate Differentials and Currency Strength
The difference between interest rates in two countries, known as the interest rate differential, is a key factor in forex trading. Traders often compare the interest rates of two currencies in a currency pair to gauge potential market movements:
- Positive Interest Rate Differential: When one currency has a higher interest rate compared to another, it often attracts investors seeking better returns. For instance, if the U.S. has a higher interest rate than the Eurozone, investors may prefer holding USD over EUR. Thus, causing the EUR/USD pair to fall as the dollar strengthens.
- Negative Interest Rate Differential: If a country’s interest rate is lower compared to another, its currency may weaken as investors look for higher-yielding alternatives. For example, if the Bank of Japan maintains low interest rates while the Federal Reserve hikes rates, traders might prefer to hold USD over JPY, leading to a rise in the USD/JPY pair.
Impact on Carry Trade
Interest rates are central to a popular trading strategy known as the carry trade. In a carry trade, a trader borrows a currency with a low interest rate and uses it to buy a currency with a higher interest rate. The trader profits from the interest rate differential:
- Example: If the interest rate in Japan is 0.1% and in Australia it is 4.0%, a trader might borrow Japanese yen (JPY) at a low cost and convert it to Australian dollars (AUD) to invest in higher-yielding assets. This strategy increases demand for AUD and can push the AUD/JPY pair higher.
However, carry trades can be risky. If market sentiment shifts due to an unexpected rate cut or economic downturn, investors might quickly unwind their positions, leading to sharp currency movements.
Examples of Interest Rate Impact on Forex
Example 1: The Federal Reserve’s Rate Hikes and the U.S. Dollar
In 2022, the Federal Reserve embarked on an aggressive rate-hiking cycle to combat soaring inflation. As the Fed raised rates from near zero to over 4%, the U.S. dollar experienced a significant appreciation against other major currencies. The interest rate hikes increased the attractiveness of U.S. assets, drawing foreign investment and driving up the value of the USD. Pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD saw substantial declines as the euro and pound weakened against the stronger dollar.
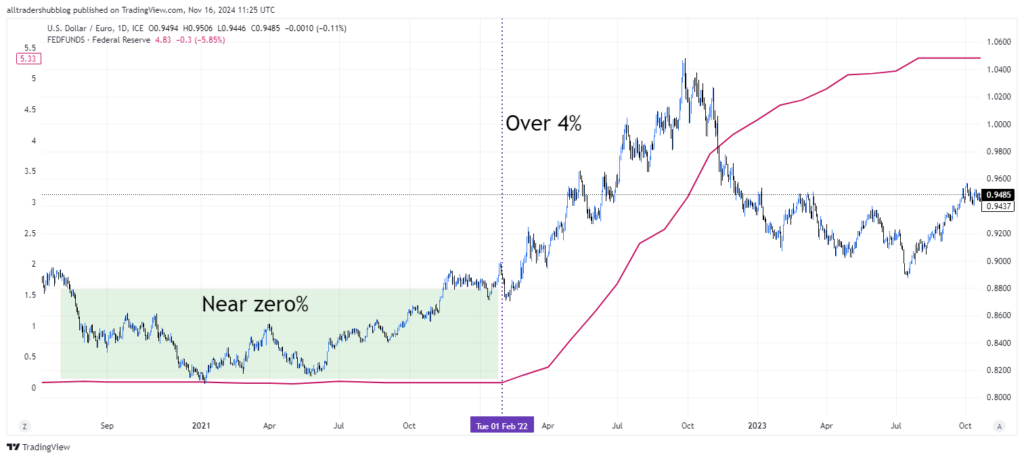
Example 2: The European Central Bank’s Low-Interest-Rate Policy
The EC kept its interest rates at historic lows for much of the 2010s to stimulate economic growth. The low rates made the euro less attractive to investors compared to higher-yielding currencies. As a result, the EUR/USD pair remained under pressure for years struggling to gain significant ground against the dollar.
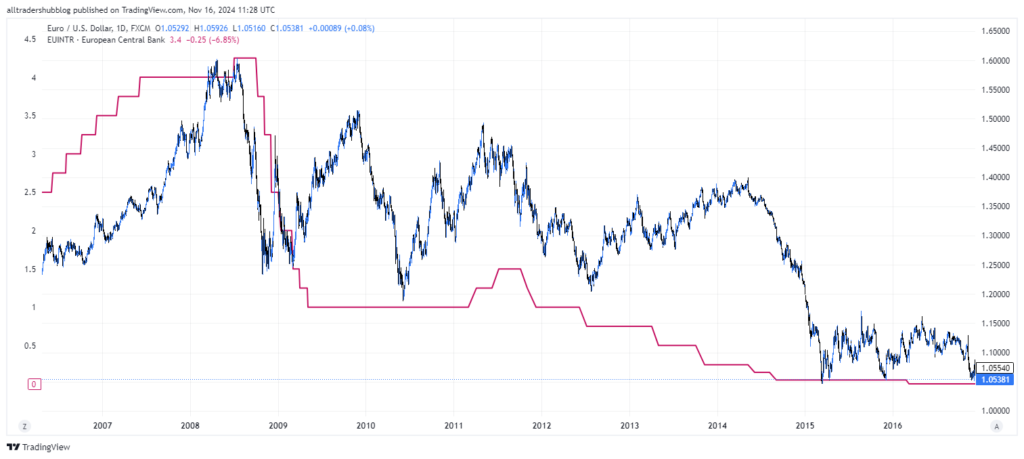
The Role of Forward Guidance in Interest Rate Expectations
Central banks often use forward guidance to communicate their future interest rate intentions. This tool helps manage market expectations and reduce uncertainty. By providing hints about upcoming rate changes, central banks can influence currency values even before any actual rate adjustments occur.
- Hawkish Forward Guidance: If a central bank indicates that it plans to raise rates soon, this is seen as hawkish, signaling economic strength. Traders may anticipate currency appreciation and adjust their positions accordingly.
- Dovish Forward Guidance: Conversely, if a central bank suggests it might cut rates or maintain low rates for an extended period, this is considered dovish. Traders may expect currency depreciation and position themselves for potential declines.
In 2021, the BoE’s hawkish statements about potential rate hikes led to a rally in the GBP, as traders anticipated tighter monetary policy.
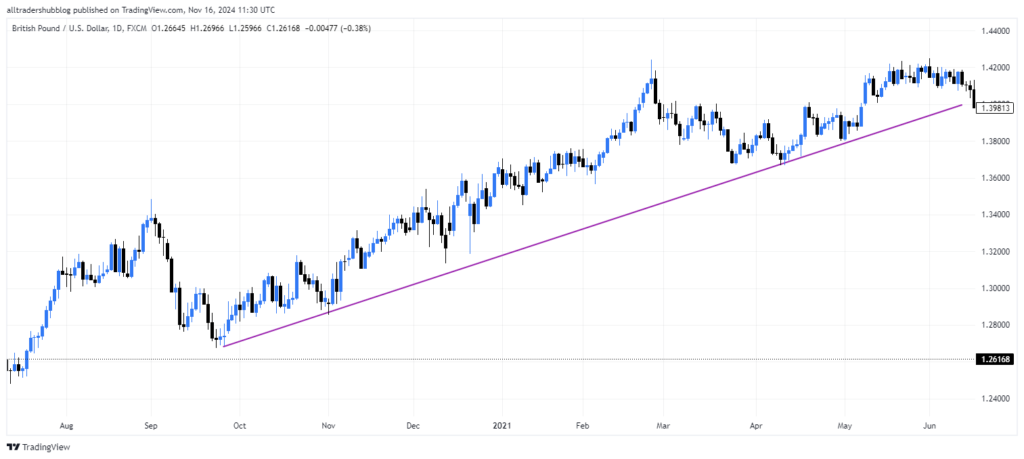
Interpreting Interest Rate Decisions as a Forex Trader
For forex traders, monitoring interest rate decisions is a critical aspect of fundamental analysis. Here are some tips for using interest rate data effectively:
- Stay Updated on Central Bank Meetings: Central bank meetings and announcements are major events in the forex calendar. Traders should follow these closely, as rate decisions and the accompanying statements can trigger significant market moves.
- Focus on Economic Data Leading Up to Decisions: Inflation reports, GDP growth data, and employment figures often influence a central bank’s decision to adjust interest rates. By analyzing these indicators, traders can better anticipate potential rate changes.
- Analyze the Interest Rate Differential: Comparing the interest rates of two currencies can help traders understand potential market trends. If a country’s rate is expected to rise while another’s remains unchanged or falls, this could signal an opportunity to trade in favor of the higher-yielding currency.
Quantitative Easing (QE) Explained
Quantitative Easing (QE) is a non-traditional monetary policy tool used by central banks to stimulate the economy during periods of low growth and low inflation. Unlike conventional interest rate adjustments, QE involves the direct injection of liquidity into the financial system.
Understanding QE is crucial for forex traders, as its implementation can significantly influence currency values and market dynamics.
What is Quantitative Easing (QE)?
Quantitative easing (QE) is when central banks buy long-term assets, such as government bonds or mortgage-backed securities. This policy increases the money supply. The main goal is to lower long-term interest rates. QE also encourages lending, investment, and economic activity. It is used when traditional policies, like lowering interest rates, are less effective. This situation occurs especially when rates are already near zero.
How QE Works:
- Asset Purchases: The central bank creates new money digitally and uses it to buy financial assets from banks and financial institutions.
- Increase in Money Supply: This process injects liquidity into the banking system, providing banks with more capital to lend to businesses and consumers.
- Lower Long-Term Interest Rates: By purchasing bonds, the central bank increases their prices and lowers their yields (interest rates). This makes borrowing cheaper for consumers and businesses, encouraging spending and investment.
- Boost in Economic Activity: With lower borrowing costs, businesses can invest more, and consumers are more likely to take loans for big purchases, driving economic growth.
The Impact of QE on Currency Values
Quantitative Easing can have a substantial impact on a country’s currency in the forex market. Here’s how QE typically affects currency values:
Currency Depreciation:
When a central bank implements QE, it effectively increases the money supply, which can lead to currency depreciation. The reasons include:
- Increased Money Supply: More money circulating in the economy often leads to a reduction in its value, as the relative supply of the currency exceeds demand.
- Lower Interest Rates: By pushing down long-term interest rates, QE reduces the returns that investors can earn from holding assets denominated in that currency. Lower yields make the currency less attractive to foreign investors, reducing demand and causing it to weaken.
- Risk Sentiment: QE is usually implemented during times of economic distress or uncertainty. The perception of economic weakness can lead investors to seek safer assets or currencies, such as the U.S. dollar (USD) or Japanese yen (JPY), further weakening the currency of the country engaging in QE.
In 2015, the ECB launched a large-scale QE program to fight deflation and stimulate the Eurozone economy. This announcement caused the euro (EUR) to depreciate significantly against the U.S. dollar (USD). The increase in euros in the market lowered its value. Traders expected a weaker euro as the money supply grew.
The Global Implications of Quantitative Easing
Quantitative easing in major economies like the United States, Eurozone, or Japan can impact the global forex market. These currencies are heavily involved in global trade and investment. As a result, QE can affect other currencies and economies in multiple ways.
Spillover Effects:
When a major central bank like the Federal Reserve (Fed) implements QE, it can trigger a chain reaction in the forex market:
- Capital Flows: Investors seeking higher returns may shift capital from lower-yielding assets (in the QE-implementing country) to higher-yielding assets elsewhere. This can lead to currency appreciation in emerging markets or countries with higher interest rates.
- Currency Wars: In response to QE, other central banks may take measures to prevent their currencies from appreciating too much against the weakening currency. This could include their own QE programs or interest rate cuts, leading to a “race to the bottom” as countries try to maintain competitive exchange rates.
In 2013, the Federal Reserve hinted at tapering its QE program, triggering the “Taper Tantrum.” Global markets reacted strongly. Currencies in emerging markets, such as the Indian rupee (INR) and Brazilian real (BRL), dropped sharply. Investors anticipated higher U.S. yields and moved their capital back to the United States.
Impact on Commodity Prices:
QE can also affect commodity prices, which in turn influence commodity-linked currencies like the Australian dollar (AUD), Canadian dollar (CAD), and New Zealand dollar (NZD):
- Weaker Currency Boosts Exports: A depreciating currency makes exports cheaper and more competitive in global markets. This can boost demand for commodities priced in that currency, such as gold, oil, or agricultural products.
- Rising Commodity Prices: When the U.S. Federal Reserve implemented QE, it led to a weaker U.S. dollar, driving up the prices of dollar-denominated commodities like oil and gold. This often benefits countries that are major commodity exporters, strengthening their currencies relative to others.
Quantitative Easing and Market Sentiment
The announcement or anticipation of QE can have an immediate impact on market sentiment. Traders watch for central bank signals indicating potential QE, as the expectation alone can move markets:
- Market Rally: Equity markets often react positively to QE announcements, as the increased liquidity and lower borrowing costs are expected to stimulate economic growth. This can lead to risk-on sentiment, where investors move away from safe-haven assets and invest in riskier, higher-yielding currencies.
- Forex Volatility: QE can lead to increased volatility in the forex market, particularly if the policy decision is unexpected or larger in scale than anticipated. Currency pairs involving the currency being influenced by QE often see significant price movements, creating trading opportunities.
In 2020, the Federal Reserve launched a massive QE program to address the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. This announcement caused U.S. stock markets to surge. At the same time, the U.S. dollar weakened significantly. Traders expected prolonged low interest rates and a higher money supply.
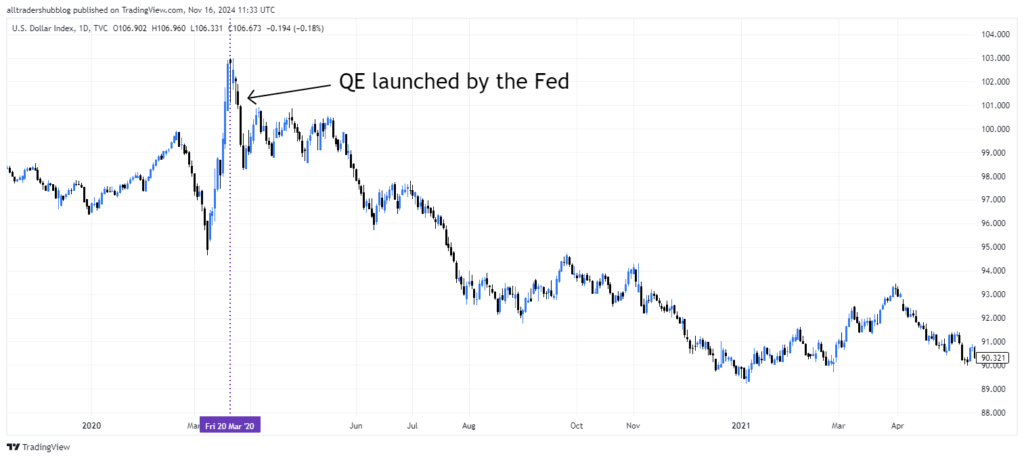
Risks and Limitations of Quantitative Easing
While QE is an effective tool for stimulating economic growth during crises, it is not without risks and limitations:
- Inflation Risk: An increase in the money supply through QE can potentially lead to higher inflation if the economy overheats. Central banks must carefully monitor inflation indicators to avoid runaway price increases.
- Diminishing Returns: Over time, QE can lose its effectiveness as interest rates approach zero or negative territory. Additional asset purchases may have less impact on lowering borrowing costs or stimulating demand.
- Debt and Financial Instability: QE can lead to increased levels of public and private debt, as lower interest rates encourage more borrowing. Excessive borrowing can create asset bubbles, such as in the housing or stock markets, increasing the risk of financial instability.
Interpreting QE Announcements as a Forex Trader
For forex traders, understanding the implications of QE is critical for making informed trading decisions:
- Monitor Central Bank Statements: Pay close attention to central bank meetings, press conferences, and economic forecasts. Central banks often provide signals about the potential for QE, giving traders a chance to anticipate market reactions.
- Analyze Economic Data: Inflation, unemployment, and GDP growth figures can indicate whether a central bank might consider implementing or expanding QE. Weak economic data may increase the likelihood of QE, while strong data may reduce it.
- Trade Currency Pairs with High Sensitivity: Focus on currency pairs that are most likely to be affected by QE, such as EUR/USD during ECB announcements or USD/JPY during Federal Reserve actions.
The Relationship Between Inflation and Central Bank Policy
Inflation is one of the most critical factors influencing central bank policy decisions. For forex traders, understanding the link between inflation and central bank actions is key to predicting currency movements. Central banks use a variety of tools to control inflation, and their policy decisions can significantly impact forex markets.
What is Inflation?
Inflation refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, eroding purchasing power. In simpler terms, as inflation increases, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Inflation is typically measured using key economic indicators like:
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): Tracks the average change in prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services.
- Producer Price Index (PPI): Measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers for their output.
- Core Inflation: Excludes volatile food and energy prices to provide a clearer view of underlying inflation trends.
Most central banks, like the Federal Reserve (Fed), the European Central Bank (ECB), and the Bank of England (BoE), target a specific inflation rate (commonly around 2%). This target is considered optimal for economic growth, as it encourages spending and investment without causing runaway price increases.
How Central Banks Respond to Inflation
Central banks play a pivotal role in managing inflation through monetary policy. Their main objective is to maintain price stability, which is crucial for sustainable economic growth. Here’s how they typically respond to different inflationary environments:
Tightening Monetary Policy (Hawkish Stance)
When inflation is rising above the central bank’s target, policymakers often adopt a hawkish stance, tightening monetary policy to curb inflationary pressures. The main tools they use include:
- Raising Interest Rates: By increasing interest rates, central banks make borrowing more expensive. This reduces consumer spending and business investments, slowing down the economy and reducing inflation.
- Impact on Currency: Higher interest rates generally lead to a stronger currency, as higher yields attract foreign investors seeking better returns, increasing demand for the currency.
- Example: In 2022, the U.S. Federal Reserve raised interest rates multiple times to combat soaring inflation. This led to a significant appreciation of the U.S. dollar against other major currencies.
- Reducing Money Supply: Central banks may also reduce the money supply through mechanisms like reducing their balance sheet or selling assets (often bonds) acquired during Quantitative Easing (QE).
- Impact on Currency: A reduced money supply often leads to currency appreciation, as the reduced availability of the currency increases its value.
Easing Monetary Policy (Dovish Stance)
Conversely, when inflation is below the target, or there is a risk of deflation, central banks may adopt a dovish stance, easing monetary policy to stimulate economic activity:
- Lowering Interest Rates: Central banks reduce interest rates to make borrowing cheaper, encouraging consumer spending and business investment, which can help push inflation towards the target.
- Impact on Currency: Lower interest rates typically lead to a weaker currency, as investors seek higher returns elsewhere, reducing demand for the lower-yielding currency.
- Example: In 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many central banks, including the ECB and the Bank of England, slashed interest rates to support their economies, leading to a depreciation of the euro (EUR) and the British pound (GBP).
- Quantitative Easing (QE): In cases where interest rates are already near zero, central banks may implement QE to inject liquidity into the economy, increasing spending and inflation.
- Impact on Currency: As explained in the previous section, QE usually leads to currency depreciation due to the increased money supply.
Inflation Expectations and Market Reactions
Inflation expectations are key in shaping central bank policies and market reactions. When traders expect higher inflation, they anticipate central banks may raise interest rates. This can lead to currency value changes before official policy decisions.
In early 2021, rising inflation expectations in the U.S. led traders to predict an earlier rate hike by the Federal Reserve. This speculation caused the U.S. dollar to rise against currencies like the Japanese yen (JPY) and euro (EUR). Investors priced in the possibility of tighter monetary policy.
Central Bank Communication and Forward Guidance
Central banks often use forward guidance to communicate their inflation outlook and potential policy actions to the market. Forward guidance is a tool that helps set market expectations by providing insights into the central bank’s future policy intentions based on current and projected economic conditions.
- Impact on Forex Markets: Clear forward guidance can reduce market uncertainty and volatility by giving traders a better idea of future interest rate paths. For instance, if a central bank signals that rate hikes are likely due to rising inflation, traders may anticipate a stronger currency.
- Example: In 2019, the European Central Bank provided forward guidance indicating that interest rates would remain low for an extended period due to subdued inflation. This dovish stance led to a weakening of the euro as traders adjusted their expectations for future rate increases.
Inflation’s Role in Currency Valuation
Inflation is a fundamental driver of currency value in the forex market. Here’s why:
- Purchasing Power Parity (PPP): This economic theory suggests that in the long term, exchange rates should move towards levels that equalize the purchasing power of different currencies. Higher inflation in one country relative to another tends to weaken its currency, as the higher price level erodes purchasing power.
- Interest Rate Differentials: Inflation affects interest rate differentials between countries, a key factor in determining currency movements. Currencies with higher interest rates (often resulting from higher inflation) tend to appreciate against those with lower rates, as investors seek higher yields.
Example: The Turkish lira (TRY) experienced significant depreciation in recent years due to high inflation rates and unconventional monetary policy. While inflation soared, interest rates were not raised sufficiently to combat the price increases, leading to a loss of confidence in the lira and its subsequent weakening against major currencies like the USD and EUR.
The Balancing Act of Central Banks
Central banks face a delicate balancing act when managing inflation. On one hand, they aim to keep inflation at a target level that supports sustainable economic growth. On the other hand, they must avoid overly aggressive measures that could stifle economic activity or create financial instability.
- Hawkish vs. Dovish Dilemma: Central banks often need to choose between a hawkish stance (focusing on reducing inflation) and a dovish stance (prioritizing economic growth). The choice depends on the broader economic context and the central bank’s priorities.
- Forex Market Implications: Traders closely monitor central bank statements and economic data releases to gauge whether a central bank is likely to adopt a hawkish or dovish stance. These expectations can drive significant movements in forex markets as traders adjust their positions based on anticipated policy changes.
The Market Impact of Central Bank Announcements
Central bank announcements are some of the most highly anticipated events in the forex market. The decisions made by central banks regarding interest rates, quantitative easing (QE), and other monetary policies can cause significant volatility and price movements in currency pairs. For forex traders, understanding the potential impact of these announcements is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
Types of Central Bank Announcements
Central banks regularly communicate with the public through various announcements, each with different levels of market impact. The main types include:
- Interest Rate Decisions:
- Market Impact: Changes in interest rates can have an immediate effect on currency values. A surprise rate hike can cause a currency to strengthen as it indicates tightening monetary policy, while a rate cut can lead to currency depreciation due to a more dovish stance.
- Monetary Policy Statements and Press Conferences:
- Market Impact: The tone of these statements—whether hawkish or dovish—can significantly influence market sentiment. Traders look for clues on future rate hikes, QE programs, and the central bank’s economic assessment.
- Forward Guidance:
- Market Impact: Clear and consistent forward guidance can stabilize market expectations and reduce volatility. However, any deviations from the expected guidance can lead to sharp market reactions.
- Quantitative Easing Announcements:
- Market Impact: The initiation or expansion of QE programs usually leads to currency depreciation as it increases the money supply. Conversely, announcements about tapering QE can lead to currency appreciation as it signals a tightening of monetary policy.
Immediate Market Reactions: Volatility and Spikes
Central bank announcements often lead to immediate and significant reactions in the forex market. The release of a new policy statement or a surprise decision can cause:
- Price Spikes: Traders rapidly adjust their positions in response to unexpected changes in interest rates or policy tone, leading to sharp price movements in affected currency pairs.
- Increased Volatility: Even anticipated announcements can cause heightened volatility as traders interpret the details of the statement and assess its implications for future monetary policy.
In March 2023, when the Federal Reserve delivered a more hawkish than expected rate hike, the U.S. dollar experienced a rapid increase in value against the euro, causing the EUR/USD pair to drop significantly within minutes of the announcement.
Longer-Term Market Impact: Trend Shifts
Beyond immediate reactions, central bank announcements can set the tone for longer-term trends in the forex market:
- Interest Rate Cycles: A series of interest rate hikes or cuts usually signals the start of a broader monetary policy cycle, influencing currency trends over months or even years. For instance, if a central bank is expected to continue raising rates, the currency is likely to appreciate in anticipation of higher returns for investors.
- Market Sentiment: The broader sentiment shaped by central bank policies—whether risk-on (optimistic about economic growth) or risk-off (pessimistic about economic conditions)—can influence currency movements. A dovish central bank may lead to a weaker currency and a preference for safe-haven assets like gold or the Japanese yen.
During the global financial crisis of 2008, aggressive rate cuts and QE programs by the U.S. Federal Reserve led to a prolonged period of dollar weakness as investors sought higher-yielding assets in emerging markets.
The Role of Market Expectations and Surprises
The impact of central bank announcements is often determined not just by the decisions made but by how those decisions compare to market expectations:
- Expected Announcements: If a central bank’s decision aligns with market expectations, the market reaction may be muted, as traders have already priced in the expected outcome.
- Surprise Announcements: Unexpected changes in policy can lead to sharp market movements. For example, a surprise rate hike can lead to a sudden appreciation of a currency as traders rush to adjust their positions in light of the new information.
In January 2015, the Swiss National Bank (SNB) unexpectedly removed its currency peg against the euro, leading to a dramatic appreciation of the Swiss franc (CHF) against all major currencies. This move, which caught the market by surprise, caused massive volatility and major losses for many traders.
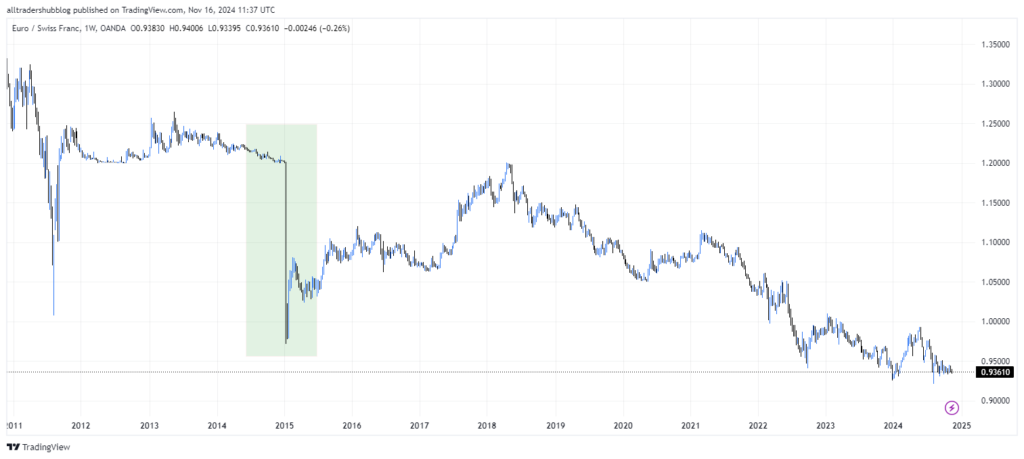
Strategies for Trading Central Bank Announcements
Given the potential impact of central bank announcements, traders often develop strategies to take advantage of the resulting volatility:
- Pre-Announcement Positioning: Some traders take positions based on their expectations of the announcement’s outcome, using economic indicators and previous central bank statements to gauge likely decisions.
- Post-Announcement Trading: Other traders prefer to wait for the announcement, then trade based on the market’s reaction. This approach reduces the risk of being caught on the wrong side of an unexpected decision but requires quick response times and a good understanding of market sentiment.
- Hedging Strategies: To protect against unexpected volatility, traders may use hedging techniques, such as options or stop-loss orders, to limit potential losses during central bank events.
A forex trader anticipating a dovish announcement from the ECB might short the euro against the U.S. dollar (EUR/USD), expecting the pair to decline as the market prices in a prolonged period of low interest rates in the Eurozone.
Trading Strategies Based on Central Bank Policies
Here are several trading strategies focused on central bank policies:
Interest Rate Differential Strategy
Concept: The interest rate differential strategy involves trading currency pairs based on the differences in interest rates set by their respective central banks. Traders look to buy currencies with higher interest rates and sell those with lower rates, benefiting from the “carry trade.”
How It Works:
- Carry Trade: In a typical carry trade, a trader borrows a low-yielding currency (e.g., Japanese yen, JPY) and uses the proceeds to buy a higher-yielding currency (e.g., Australian dollar, AUD).
- Interest Rate Expectations: If a central bank signals future rate hikes, the currency is likely to appreciate due to increased demand, as investors seek higher returns.
Example: In 2021, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) raised interest rates, leading to a stronger New Zealand dollar (NZD). Traders anticipating this move could have gone long on NZD/USD, benefiting from both the interest rate differential and the appreciation of the NZD.
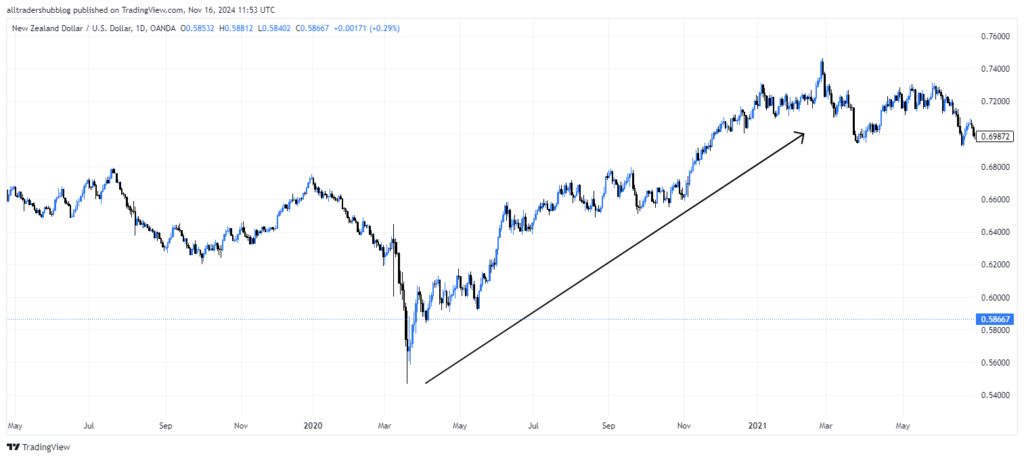
Risks: This strategy can be risky during periods of high market volatility or when central banks shift unexpectedly from their stated policies, causing rapid currency movements that can lead to significant losses.
Trading Based on Quantitative Easing Announcements
Concept: Quantitative easing (QE) typically involves central banks purchasing large amounts of financial assets to inject liquidity into the economy. This policy tends to weaken a currency as it increases the money supply, making the currency less scarce.
How It Works:
- Entry Signal: Traders look for central bank announcements signaling the start or continuation of QE. This typically leads to a depreciation of the currency due to increased supply.
- Exit Signal: The tapering or end of QE is usually a signal for traders to close their short positions, as the currency may start to appreciate with reduced money supply.
Example: When the European Central Bank (ECB) announced its QE program in 2015, the euro (EUR) weakened significantly against major currencies like the U.S. dollar (USD). Traders who shorted EUR/USD during this period could have profited from the prolonged downtrend driven by the QE policy.
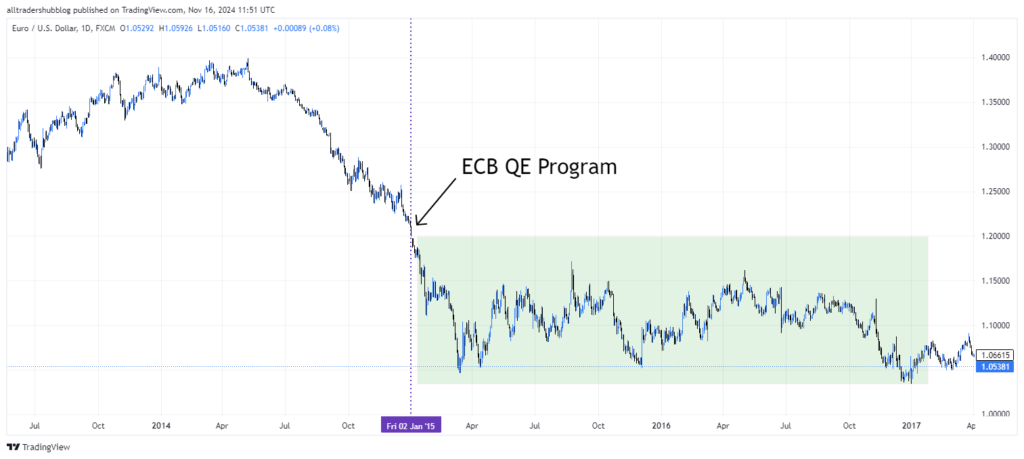
Risks: Unexpected economic changes, such as a sudden rise in inflation or geopolitical events, may prompt central banks to adjust their QE programs quickly, potentially leading to sharp reversals in currency trends.
News Trading Strategy: Reacting to Central Bank Announcements
Concept: News trading involves making quick trades based on the outcomes of central bank announcements. This strategy requires the trader to react swiftly to changes in interest rates, forward guidance, or other monetary policy decisions.
How It Works:
- Before the Announcement: Traders analyze economic indicators (e.g., inflation, employment data) to gauge what the central bank might announce.
- During the Announcement: Traders monitor live updates from central bank meetings and make immediate decisions based on the statements given. For instance, if a rate hike is announced unexpectedly, traders might buy the currency in anticipation of its appreciation.
- After the Announcement: Traders adjust their positions based on the market’s reaction. If the market overreacts, it might present an opportunity for a counter-trend trade.
Example: In September 2022, the Federal Reserve announced a larger-than-expected rate hike, leading to an immediate surge in the U.S. dollar (USD) against other currencies. Traders using a news trading strategy could have capitalized on this spike by buying USD pairs like USD/JPY.
Risks: The high volatility surrounding central bank announcements can lead to rapid price swings, making it challenging to execute trades at desired levels. Slippage and increased spreads are common during these times.
Position Trading Based on Forward Guidance
Concept: Position trading involves holding trades over an extended period, based on the expected trajectory of central bank policies. Traders use forward guidance from central banks to anticipate long-term interest rate trends and monetary policy directions.
How It Works:
- Analyzing Forward Guidance: Traders listen to central bank statements to understand their outlook on economic conditions and policy direction.
- Long-Term Trend Identification: Based on the forward guidance, traders take positions that align with the expected long-term trend. For example, if a central bank signals a series of upcoming rate hikes, a trader might go long on the currency.
- Holding Period: Position traders hold their trades for weeks or months, adjusting as new economic data and central bank statements provide updated information.
Example: In 2019, the Bank of Canada signaled a pause in rate hikes due to economic uncertainties, leading to a weakening of the Canadian dollar (CAD). Position traders shorting CAD against the USD (USD/CAD) benefited from the currency’s depreciation over the following months.
Risks: Long-term trades are exposed to unexpected market events and economic shifts, such as sudden geopolitical tensions or financial crises, which can disrupt the anticipated trend.
Combining Central Bank Policies with Technical Analysis
Concept: While central bank policies provide fundamental insights, combining them with technical analysis can help traders refine their entry and exit points.
How It Works:
- Fundamental Signal: Traders identify a fundamental signal, such as a central bank indicating future rate hikes.
- Technical Confirmation: They then look for technical confirmation, such as a breakout from a key resistance level or a bullish reversal pattern on the chart.
- Entry and Exit Points: Technical analysis helps in determining precise entry points, stop-loss levels, and profit targets, reducing the risk of entering trades solely based on fundamental data.
Example: In April 2023, the ECB hinted at continuing its rate hike cycle. Traders who identified this as a bullish signal for the euro could have looked for a technical breakout in the EUR/USD chart to confirm the trade and set a favorable entry point.
Risks: Relying on technical analysis alone without understanding the broader context of central bank policies can lead to false signals. Therefore, combining both approaches provides a more comprehensive strategy.
Risk Management in Central Bank Policy Trading
Given the high volatility associated with central bank announcements, risk management is essential:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Set stop-loss orders to protect against sudden reversals caused by unexpected policy changes.
- Position Sizing: Use smaller position sizes to manage the increased risk during central bank events.
- Avoid Overtrading: Focus on high-probability setups rather than attempting to trade every central bank announcement, which can lead to significant losses if the market moves unpredictably.
Example: In 2021, when the Reserve Bank of Australia unexpectedly maintained its dovish stance, traders who had tight stop-loss orders were able to limit their losses as the AUD/USD pair dropped sharply.
Key Central Banks and Their Policy Trends
Not all central banks carry equal weight. Some, due to the size of their economies and the influence of their currencies, have an outsized impact on global financial markets. Understanding the policy trends of these key central banks is crucial for traders who rely on fundamental analysis to anticipate currency movements.
Here, we will explore the monetary policies and recent trends of the most influential central banks in the world:
The Federal Reserve (Fed) – United States
The Federal Reserve, or the Fed, is the central bank of the United States and arguably the most influential central bank in the world. Its policy decisions affect the U.S. dollar (USD), the world’s primary reserve currency, making it a focal point for forex traders.
Policy Focus:
- Dual Mandate: The Fed’s main objectives are to maintain price stability (targeting around 2% inflation) and maximize employment.
- Interest Rate Decisions: The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meets regularly to decide on the federal funds rate, which directly impacts short-term interest rates and the overall cost of borrowing in the U.S. economy.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): The Fed has used QE as a tool to stimulate the economy during downturns, purchasing large amounts of government securities to inject liquidity into the financial system.
Recent Trends:
- 2022-2023 Tightening Cycle: The Fed embarked on an aggressive rate-hiking cycle in response to surging inflation, raising interest rates from near zero to multi-decade highs. This led to a strong appreciation of the USD as higher rates attracted foreign investment.
- Forward Guidance: Traders closely watch Fed Chair statements and FOMC meeting minutes for hints on future rate hikes or cuts, which can cause significant volatility in forex markets.
Impact on Forex Pairs:
- The Fed’s tightening policy has typically strengthened the USD, impacting pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY.
- In contrast, dovish stances tend to weaken the USD, benefiting currencies like the euro (EUR) and the Japanese yen (JPY).
The European Central Bank (ECB) – Eurozone
The European Central Bank (ECB) manages monetary policy for the Eurozone, a region consisting of 20 European Union member countries that use the euro (EUR) as their official currency.
Policy Focus:
- Price Stability: The ECB aims to keep inflation close to, but below, 2%.
- Interest Rates: The ECB’s main policy rates include the refinancing rate, deposit facility rate, and marginal lending rate, which it adjusts to influence economic activity.
- Quantitative Easing: The ECB has implemented various asset purchase programs to support the Eurozone economy, particularly during the European debt crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Recent Trends:
- Normalization of Policy: Following years of negative interest rates, the ECB began normalizing its policy in 2022, raising rates to combat high inflation driven by energy costs and supply chain disruptions.
- Focus on Inflation: The ECB’s primary concern has been bringing down inflation, which has remained above its target due to factors like energy price shocks and supply chain constraints.
Impact on Forex Pairs:
- Hawkish policies from the ECB tend to strengthen the euro, affecting pairs like EUR/USD and EUR/GBP.
- Dovish policies, such as maintaining or lowering rates, often weaken the euro, benefiting currencies like the USD and GBP.
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) – Japan
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) is known for its ultra-loose monetary policies, particularly its long-standing approach of maintaining negative interest rates and implementing large-scale quantitative easing.
Policy Focus:
- Price Stability and Economic Growth: The BoJ aims for stable prices and economic growth, with a particular focus on ending decades of deflation.
- Yield Curve Control (YCC): The BoJ’s YCC policy targets the 10-year government bond yield, aiming to keep it around zero to stimulate economic activity.
- Quantitative and Qualitative Easing: The BoJ has been a pioneer in using QE to boost liquidity and support economic growth.
Recent Trends:
- Continued Dovish Stance: Despite inflation rising above its target in 2022, the BoJ maintained its dovish stance, citing the need for sustainable wage growth before tightening policy.
- Intervention in Forex Markets: In 2022, the BoJ intervened to support the yen (JPY) as it depreciated sharply against the USD, driven by widening interest rate differentials.
Impact on Forex Pairs:
- The BoJ’s dovish policies tend to weaken the yen, affecting pairs like USD/JPY and EUR/JPY.
- Market interventions by the BoJ can lead to sharp, unexpected movements in yen pairs, offering opportunities and risks for traders.
The Bank of England (BoE) – United Kingdom
The Bank of England (BoE) is the central bank of the UK and plays a key role in determining the value of the British pound (GBP) through its monetary policy decisions.
Policy Focus:
- Inflation Control: The BoE targets an inflation rate of 2% and adjusts its policy tools accordingly.
- Interest Rates: The BoE’s main tool is the Bank Rate, which influences borrowing costs throughout the economy.
- Asset Purchases: The BoE has engaged in asset purchases during economic downturns to provide liquidity and stimulate growth.
Recent Trends:
- Inflation-Fighting Measures: In response to high inflation in 2022-2023, driven by energy price shocks and supply chain issues, the BoE raised interest rates multiple times, despite concerns about economic growth.
- Brexit Impact: The BoE’s policies have also been influenced by the economic uncertainties arising from Brexit, which has led to increased volatility in GBP pairs.
Impact on Forex Pairs:
- Hawkish stances by the BoE tend to strengthen the GBP, affecting pairs like GBP/USD and EUR/GBP.
- Dovish stances or concerns about economic growth can weaken the GBP, benefiting the USD and EUR.
The People’s Bank of China (PBoC) – China
While not as transparent as Western central banks, the People’s Bank of China (PBoC) plays a crucial role in managing the Chinese yuan (CNY) and influencing global currency markets.
Policy Focus:
- Economic Stability: The PBoC focuses on maintaining economic stability, controlling inflation, and supporting growth.
- Exchange Rate Management: The PBoC manages the CNY’s exchange rate through a “managed float” system, intervening in the forex market as needed.
- Credit and Liquidity Control: The PBoC adjusts reserve requirements and lending rates to control credit availability in the economy.
Recent Trends:
- Monetary Easing: In response to economic slowdowns and the impact of COVID-19, the PBoC implemented monetary easing measures, including cutting reserve requirements and reducing key interest rates.
- Currency Intervention: The PBoC has occasionally intervened to stabilize the CNY, particularly when faced with capital outflows or trade tensions.
Impact on Forex Pairs:
- PBoC policies significantly impact emerging market currencies, particularly those in Asia. Movements in CNY often influence pairs like USD/CNY and AUD/CNY.
- Traders also watch PBoC policy changes for broader market impacts, as China’s economy is a major driver of global trade.
Conclusion
Central bank policies are major drivers of currency movements in the forex market. By understanding these policies, traders can better predict market reactions. This helps them capitalize on potential shifts. Central banks, like the Federal Reserve, ECB, Bank of Japan, Bank of England, and People’s Bank of China, impact currency strength and investor sentiment. Their actions, from interest rate changes to quantitative easing, have a profound effect on global markets.
Each central bank’s approach varies based on its economic goals, domestic conditions, and global economic environment. By monitoring central bank announcements and understanding their broader economic implications, traders can develop more accurate forecasts and strategic plans for their trades.
For forex traders, incorporating central bank policy insights helps clarify potential currency trends. Key indicators like interest rates, inflation, and quantitative easing are crucial. By focusing on these, traders can make informed decisions and anticipate market volatility. This approach helps navigate the complex forex market more effectively. In a constantly changing economic environment, staying attuned to central bank actions is essential for a successful forex strategy.
