The yield curve is a crucial indicator in financial markets, reflecting the relationship between short-term and long-term interest rates. It serves as a barometer of economic expectations, influencing investment decisions, monetary policy, and market sentiment.
For forex traders, the yield curve provides valuable insights into future interest rate trends and economic conditions, which can directly impact currency valuations. By analyzing the yield curve, traders can anticipate potential shifts in monetary policy, assess risk sentiment, and refine their forex trading strategies.
This article explores how the yield curve impacts the forex market, focusing on its patterns, significance, and trading implications.
1. Understanding the Yield Curve
The yield curve is a graphical representation that plots the yields (interest rates) of Treasury securities with different maturities. It compares short-term Treasury bills with longer-term Treasury notes and bonds, providing insight into investor expectations about future economic conditions.
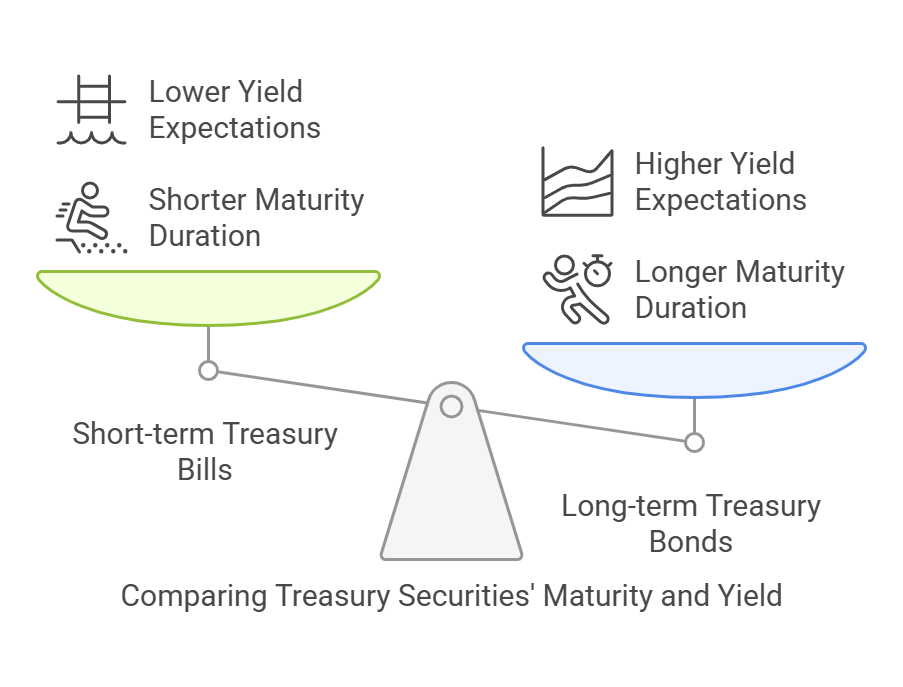
Components of the Yield Curve
- Short-term Treasury bills: Represent government debt instruments with maturities of one year or less.
- Long-term Treasury bonds: Include government securities with maturities of 10 years or more.
- Yield: The interest rate return an investor receives for holding a bond until maturity.
How the Yield Curve is Derived
The yield curve is derived from the closing market prices of Treasury securities in the over-the-counter market. It reflects investor sentiment about inflation, economic growth, and interest rate expectations.
Typical Shape of the Yield Curve
- A normal yield curve typically slopes upward, as investors demand higher returns for longer-term bonds due to increased risk.
- The shape of the yield curve can change based on economic conditions and monetary policy decisions by central banks, influencing investor behavior and forex markets.
2. Yield Curve Patterns and Their Significance
The shape of the yield curve provides key insights into economic conditions and future interest rate movements. Each pattern has specific implications for forex traders.
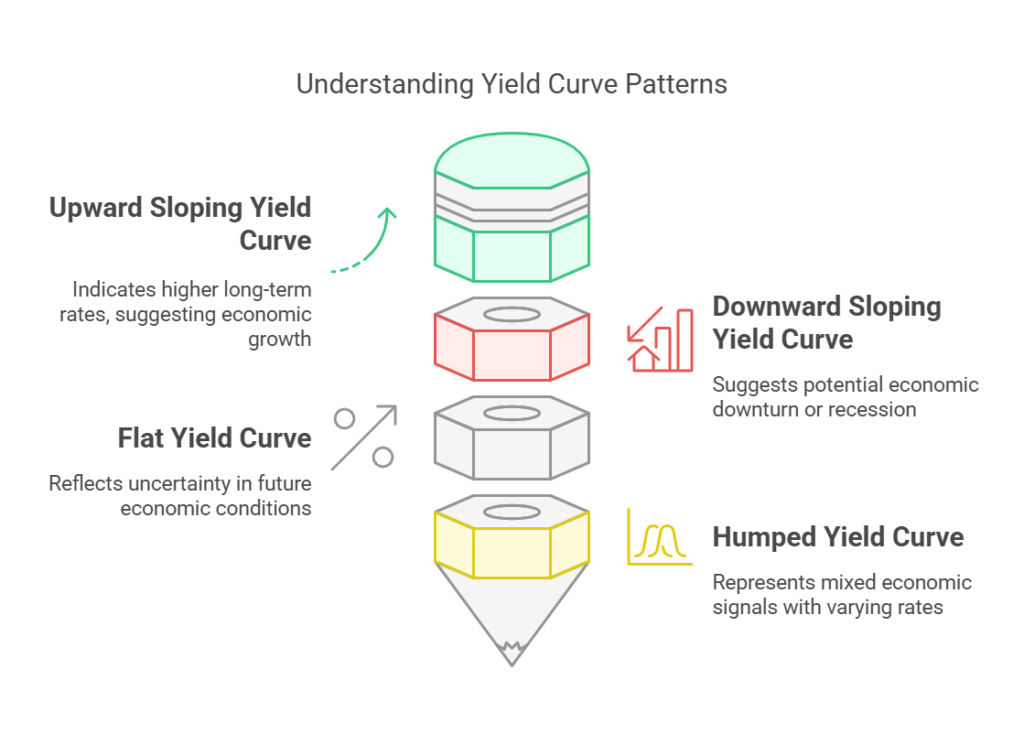
a) Upward Sloping Yield Curve (Normal Yield Curve)
An upward-sloping yield curve occurs when long-term interest rates are higher than short-term rates. This is the most common yield curve shape and indicates:
- Expectations of future economic growth.
- Potential inflationary pressures as the economy expands.
- Higher interest rates in the future, which can make a currency more attractive to investors.
Forex Implications:
- A country with a steepening yield curve may see its currency appreciate as investors anticipate stronger economic growth and higher interest rates.
- Traders often favor currencies from economies with rising long-term yields, expecting central banks to tighten monetary policy.
b) Downward Sloping Yield Curve (Inverted Yield Curve)
An inverted yield curve occurs when short-term interest rates are higher than long-term rates. This phenomenon is rare and often signals:
- Economic contraction or an impending recession.
- Declining inflation expectations.
- A potential central bank rate cut to stimulate economic activity.
Forex Implications:
- An inverted yield curve can lead to currency depreciation as investors anticipate lower future interest rates.
- Forex traders may reduce exposure to currencies of countries with an inverted yield curve, shifting capital to safer assets.
- If multiple major economies experience an inverted yield curve, risk-off sentiment may drive investors toward safe-haven currencies like the US dollar (USD) or Japanese yen (JPY).
c) Flat Yield Curve
A flat yield curve occurs when short-term and long-term interest rates are nearly equal. This typically reflects:
- Market uncertainty about future economic growth.
- A transition between an upward or downward trend.
- Expectations of stable monetary policy in the near term.
Forex Implications:
- A flat yield curve suggests a balanced market outlook, leading to mixed forex movements.
- Traders assess other macroeconomic indicators to determine whether the currency will strengthen or weaken.
- If one country’s yield curve flattens while another’s steepens, forex traders may favor the currency with the steeper curve, expecting higher returns.
d) Humped Yield Curve
A humped or bell-shaped yield curve occurs when medium-term interest rates are higher than both short-term and long-term rates. This pattern is less common and may indicate:
- Market uncertainty and volatility.
- A potential turning point in interest rate trends.
- Speculation about future central bank interventions.
Forex Implications:
- Currencies associated with economies experiencing a humped yield curve may face unpredictable fluctuations.
- Traders may avoid long-term commitments in such currencies due to increased uncertainty.
- Hedging strategies become essential in forex trading when yield curves display erratic behavior.

3. How Forex Traders Use the Yield Curve
Forex traders use the yield curve to anticipate interest rate changes and adjust their trading strategies accordingly. The following are key ways traders incorporate yield curve analysis into their decision-making.
a) Interest Rate Differentials
Interest rate differentials—the difference between two countries’ interest rates—are a major driver of currency movements. Since yield curves reflect interest rate expectations:
- A steepening yield curve suggests higher future rates, making a currency more attractive to investors.
- A flattening or inverting yield curve signals lower future rates, potentially weakening a currency.
- Traders monitor yield spreads between different economies to identify profitable forex opportunities.
b) Central Bank Policies
Central banks adjust interest rates based on economic conditions, often guided by yield curve trends. Forex traders analyze yield curve shifts to:
- Predict central bank rate decisions.
- Position trades ahead of monetary policy announcements.
- Assess the likelihood of rate hikes or cuts, which influence currency demand.
c) Carry Trade Strategy
The carry trade involves borrowing in a low-interest-rate currency and investing in a higher-yielding one. Yield curve analysis helps traders:
- Identify currencies with strong interest rate differentials.
- Determine the sustainability of carry trades based on future rate expectations.
- Avoid risks associated with sudden interest rate reversals.
d) Trend Following Strategies
Yield curves provide insight into long-term trends in forex markets. Traders use this information to:
- Align trades with fundamental economic trends.
- Hedge currency exposure by adjusting positions according to yield curve movements.
- Combine yield curve insights with technical analysis for informed decision-making.
e) Breakout Trading
Forex traders also use yield curve analysis to anticipate sharp currency movements caused by changing economic sentiment. A shifting yield curve may signal:
- An upcoming breakout in currency pairs.
- A shift in central bank policy leading to increased volatility.
- Key moments when traders can capitalize on market inefficiencies.
Here’s the final part of your blog with the additional analysis and conclusion sections added:
4. Additional Analysis: Yield Curve and Fundamental Indicators
While the yield curve provides valuable insights into interest rate expectations and economic sentiment, forex traders should combine it with other macroeconomic indicators for a comprehensive analysis.
Inflation Rates and Interest Rate Expectations
Inflation is a key driver of monetary policy decisions. When inflation rises, central banks may increase interest rates to control price levels, leading to changes in the yield curve. Conversely, low inflation can result in lower interest rates, affecting currency valuations.
Forex Implications:
- A rising inflation rate in a country with a steepening yield curve may signal upcoming interest rate hikes, making the currency more attractive.
- If inflation remains persistently low despite a flat or inverted yield curve, traders might anticipate future rate cuts, leading to currency depreciation.
Unemployment Data and Economic Strength
Labor market conditions are closely monitored by central banks. Low unemployment suggests economic growth and potential wage-driven inflation, influencing interest rate decisions. High unemployment, on the other hand, signals economic weakness and potential monetary easing.
Forex Implications:
- A country with low unemployment and a steepening yield curve may see increased investor confidence in its currency.
- Rising unemployment alongside an inverted yield curve can reinforce recession fears, leading to capital flight from that currency.
GDP Growth and Trade Balances
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth measures economic performance, while trade balances indicate a country’s competitiveness in global markets. Both factors interact with yield curve movements to shape forex trends.
Forex Implications:
- Strong GDP growth and a steep yield curve may boost demand for a country’s currency.
- A declining trade balance combined with a flat or inverted yield curve may signal economic trouble, leading to currency depreciation.
Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis
While fundamental analysis (including yield curve interpretation) provides a macroeconomic perspective, technical analysis can refine trade execution. Traders use:
- Moving averages to confirm trends.
- Support and resistance levels to identify entry and exit points.
- Chart patterns to anticipate price movements aligned with fundamental drivers like interest rate differentials.
By integrating both analytical approaches, traders can develop more precise forex strategies.
Conclusion
The yield curve is a powerful tool for forex traders, offering insights into economic expectations, interest rate trends, and potential currency movements.
Key Takeaways:
- An upward-sloping yield curve signals economic growth and potential currency appreciation.
- An inverted yield curve warns of recession risks and possible currency depreciation.
- A flat yield curve suggests market uncertainty and requires additional economic analysis.
- A humped yield curve indicates volatility, making forex markets unpredictable.
Understanding how the yield curve interacts with fundamental factors—such as inflation, employment, and GDP—allows traders to anticipate central bank policies and position themselves strategically in the forex market.
Final Thought: Forex traders should consistently monitor yield curve movements, combining them with macroeconomic indicators and technical analysis to make informed trading decisions. Keeping an eye on these dynamics will enhance market timing and risk management, leading to more effective forex strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How does the yield curve impact currency exchange rates?
The yield curve influences interest rate expectations, which affect capital flows and investor sentiment. A steepening yield curve often strengthens a currency due to higher expected returns, while an inverted yield curve can signal economic weakness and potential currency depreciation.
2. Why do forex traders monitor the yield curve?
Forex traders use the yield curve to anticipate interest rate changes, central bank policies, and economic conditions. By analyzing yield curve movements, traders can identify potential shifts in currency valuations and adjust their strategies accordingly.
3. Can the yield curve predict forex market trends?
While the yield curve is not a standalone predictor, it provides valuable macroeconomic insights that, when combined with other indicators like inflation, GDP, and employment data, can help traders forecast long-term forex trends.
4. How does the yield curve affect carry trades?
The yield curve helps traders identify interest rate differentials, which are essential for carry trade strategies. A steep yield curve suggests rising interest rates, making high-yield currencies more attractive for carry trades, whereas a flattening or inverted yield curve may signal lower returns and reduced carry trade opportunities.
5. Should forex traders rely solely on the yield curve for trading decisions?
No, traders should use the yield curve alongside other fundamental and technical indicators. Economic data, geopolitical events, and market sentiment also play crucial roles in shaping currency movements, so a well-rounded approach is essential for successful forex trading.
