One of the critical elements often overlooked by novice traders is the role of bond yields in shaping forex market dynamics. While many traders focus solely on technical indicators or short-term price movements, seasoned investors know that understanding the underlying economic forces can provide a significant edge in predicting long-term trends.
In this article, we delve into the intricate relationship between bond yields and forex prices, exploring why this correlation exists and how traders can leverage it to enhance their analysis. We will break down the core concepts of bond yields, discuss key factors driving their movements, and examine examples to illustrate how shifts in yields influence major currency pairs.
By the end of this article, you will not only understand why bond yields matter in forex trading but also learn practical ways to incorporate yield analysis into your trading strategy.
What Are Bond Yields?
To understand the correlation between bond yields and forex prices, we must first grasp what bond yields are and why they are crucial to financial markets.
Bond yields represent the return an investor earns from holding a bond. Essentially, they measure the income received from an investment in bonds as a percentage of its current market price. However, the concept of bond yields is multifaceted, encompassing various types and interpretations that are important for forex traders to understand.
A. Definition of Bond Yields
At its core, a bond yield is the interest rate, or “yield,” that bondholders receive on their investment. When a government or corporation issues a bond, it promises to pay periodic interest (the “coupon“) and return the principal amount at maturity.
The yield is a function of the bond’s coupon payment and its current price:

When bond prices fall, yields rise, and vice versa. This inverse relationship occurs because the fixed coupon payment becomes more attractive when bond prices drop, effectively increasing the yield.
For traders, this fluctuation in bond yields signals changing expectations in the broader economy, particularly around inflation and interest rates.
B. Types of Bond Yields
To fully leverage bond yield analysis in forex trading, it’s essential to differentiate between the main types of bond yields:
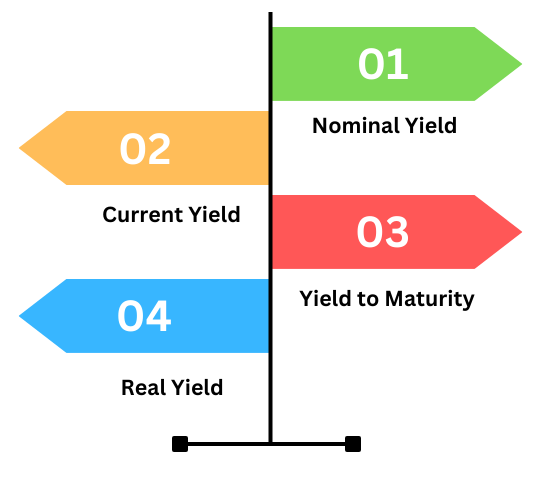
- Nominal Yield:
- The nominal yield is the simplest form, calculated as the annual coupon payment divided by the face value of the bond. It does not account for changes in the bond’s market price or inflation, making it a basic indicator of a bond’s return.
- Current Yield:
- The current yield provides a snapshot of a bond’s return based on its current market price rather than its face value. It’s more useful for traders because it reflects the bond’s present valuation and helps assess the market’s current sentiment.
- Yield to Maturity (YTM):
- Yield to maturity is the most comprehensive measure, estimating the total return an investor will receive if they hold the bond until maturity. YTM considers the bond’s current market price, coupon payments, and time to maturity, offering a holistic view of the bond’s potential return. It’s a critical indicator used by traders to evaluate long-term interest rate expectations.
- Real Yield:
- The real yield adjusts the nominal yield for inflation. It indicates the actual purchasing power of the yield, reflecting what investors will truly earn after accounting for inflation. Higher real yields can attract investors seeking better returns, influencing demand for the currency associated with that bond.
C. Factors Influencing Bond Yields
Several factors drive bond yield movements, and understanding these can help traders anticipate changes in forex prices:
- Interest Rate Changes:
- Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank (ECB), influence bond yields by setting benchmark interest rates. When central banks raise interest rates to combat inflation, bond yields typically increase, making the currency more attractive to investors.
- Inflation Expectations:
- Rising inflation erodes the purchasing power of future bond payments, leading investors to demand higher yields to compensate for this loss. Higher inflation expectations usually push bond yields up, impacting forex prices as investors seek currencies with higher real returns.
- Economic Growth Outlook:
- Strong economic growth typically leads to higher bond yields as demand for capital increases and central banks tighten monetary policy to prevent overheating. Conversely, in periods of economic slowdown, bond yields tend to fall as investors flock to safer assets, and central banks lower interest rates to stimulate growth.
- Risk Sentiment:
- The general risk sentiment in financial markets also affects bond yields. During risk-off periods, investors may seek the safety of government bonds, pushing bond prices up and yields down. In risk-on periods, when investor confidence is high, they may prefer equities or riskier assets, leading to higher yields as bond prices drop.
Understanding the Forex Market Through Fundamentals
Unlike equity markets, which are influenced primarily by company performance, the forex market is driven by broader economic forces and macroeconomic indicators. Fundamental analysis in forex involves assessing these economic factors to determine the intrinsic value of a currency. One such crucial element is the behavior of bond yields, which provides insights into interest rate expectations, economic health, and investor sentiment.
A. Key Drivers of Forex Prices
To effectively navigate the forex market, traders need to grasp the core drivers influencing currency values. These drivers are deeply connected to a country’s economic health, central bank policies, and global market sentiment. Here are some of the most significant factors:
- Interest Rates:
- Interest rates set by central banks are a primary driver of currency values. Higher interest rates typically attract foreign capital seeking higher returns, leading to an appreciation of the currency. Conversely, lower interest rates may result in currency depreciation as investors seek better yields elsewhere.
- Economic Data Releases:
- Key economic indicators, such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), employment reports, inflation data (CPI), and retail sales, provide insights into a country’s economic performance. Positive economic data generally strengthens a currency, as it indicates robust economic growth and potential interest rate hikes by the central bank. Negative data, on the other hand, can weaken a currency as it signals economic downturns or potential rate cuts.
- Inflation Rates:
- Inflation is a crucial metric for central banks, as it directly influences their monetary policy decisions. High inflation erodes purchasing power, prompting central banks to raise interest rates to curb inflationary pressures. Higher interest rates can boost a currency’s value, while low inflation often leads to lower rates and a weaker currency.
- Political Stability and Economic Policies:
- Political events and changes in government policies can create significant volatility in the forex market. For example, elections, geopolitical tensions, trade policies, and fiscal measures can all impact investor confidence and affect currency demand. Stable political environments tend to support stronger currencies, while political uncertainty can lead to capital outflows and currency depreciation.
B. Role of Interest Rate Differentials
Interest rate differentials—the difference between interest rates of two countries—are one of the most significant factors in forex trading. This differential affects the flow of capital between countries, influencing the relative value of currencies.
For instance, if the U.S. Federal Reserve raises interest rates while the European Central Bank (ECB) maintains low rates, the interest rate differential between the U.S. dollar (USD) and the euro (EUR) widens. This makes the USD more attractive to investors seeking higher returns, increasing demand for the USD and causing the EUR/USD pair to decline.
Bond yields serve as a proxy for these interest rate expectations, as they reflect market perceptions about future rate changes. When bond yields rise in one country relative to another, it suggests that investors expect higher future interest rates, prompting capital inflows into that country and boosting its currency value.
C. Why Bond Yields Matter in Forex Trading
Bond yields are a crucial indicator for forex traders because they encapsulate market expectations about future interest rates and economic performance. Central banks often adjust their policy rates based on economic conditions, and bond yields react in anticipation of these changes. For instance:
- Predicting Central Bank Actions:
- Rising bond yields often indicate that the market expects future interest rate hikes by the central bank. Forex traders monitor these signals to anticipate shifts in monetary policy, which can impact currency prices significantly.
- Reflecting Economic Sentiment:
- Bond yields also provide insights into broader economic sentiment. Higher yields generally suggest optimism about economic growth and inflation, leading to stronger currencies. Lower yields may indicate economic concerns, driving investors towards safer assets like bonds and currencies of stable economies (e.g., the USD or JPY).
- Safe Haven Demand:
- During times of economic uncertainty or market turmoil, investors often seek the safety of government bonds from stable economies, such as U.S. Treasuries or German Bunds. This “flight to quality” pushes up bond prices and lowers yields, simultaneously driving demand for the corresponding currency as a safe haven.
The Link Between Bond Yields and Forex Prices
The relationship between bond yields and forex prices is a fundamental concept in macroeconomic analysis and is critical for forex traders looking to understand currency movements. Bond yields, often seen as a proxy for interest rate expectations, reflect the market’s perception of economic health, inflation, and central bank policy.
As these factors play a significant role in shaping forex market dynamics, changes in bond yields can directly impact currency valuations.
A. Interest Rate Expectations
One of the primary reasons bond yields are closely watched in forex markets is their ability to signal future interest rate movements. Here’s how this works:
Anticipating Central Bank Policy:
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank (ECB), use interest rates as a tool to control inflation and stabilize the economy. Bond yields often move in anticipation of central bank actions. For instance, if bond yields rise, it may indicate that investors expect the central bank to increase interest rates in the near future, making the currency more attractive.
Yield Differentials and Currency Valuation:
Traders look at yield differentials, which are the differences between bond yields of two countries. If U.S. Treasury yields rise relative to Japanese Government Bond (JGB) yields, it suggests that the U.S. offers a more attractive investment opportunity. This could lead to a stronger USD/JPY pair as investors buy USD to purchase U.S. bonds.
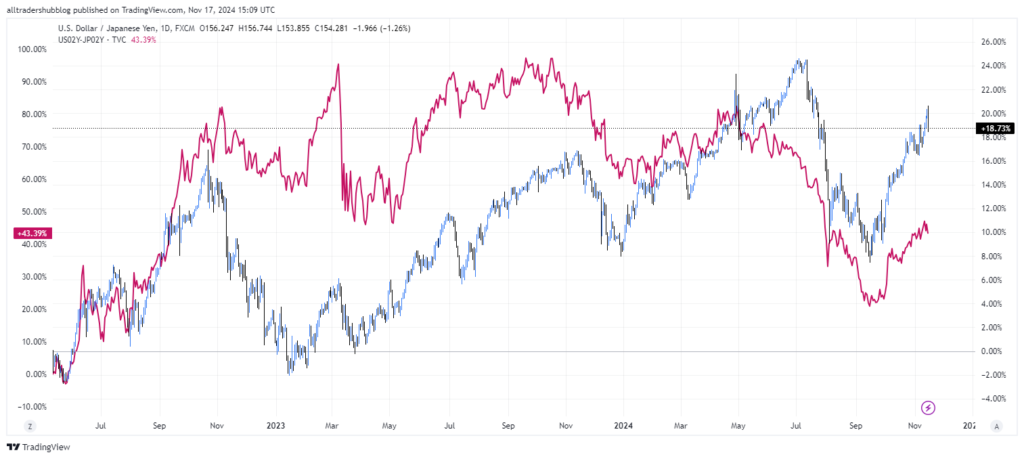
Carry Trade Opportunities:
Bond yields also play a crucial role in carry trades, a strategy where investors borrow in a low-yielding currency to invest in a higher-yielding one. For instance, if Australian bond yields are higher than Japanese yields, traders might borrow in JPY and invest in AUD, increasing demand for the Australian dollar.
B. Safe Haven Flows and Risk Sentiment
The correlation between bond yields and forex prices is also influenced by market sentiment, particularly during periods of heightened uncertainty or risk aversion. Here’s how this dynamic unfolds:
- Safe Haven Demand:
- In times of economic uncertainty or geopolitical turmoil, investors tend to flock to safe-haven assets such as U.S. Treasuries or German Bunds. This flight to safety pushes bond prices up and yields down. Simultaneously, the demand for safe-haven currencies like the USD or Swiss franc (CHF) increases, causing these currencies to appreciate against riskier ones like the Australian dollar (AUD) or New Zealand dollar (NZD).
- Risk-On vs. Risk-Off Sentiment:
- In a risk-on environment, where investors are confident about economic growth, they tend to move away from safe-haven assets and towards equities and higher-yielding currencies. This scenario usually leads to rising bond yields as bond prices fall due to reduced demand. Conversely, in a risk-off environment, investors seek the safety of bonds and safe-haven currencies, leading to lower yields and strengthening of currencies like the USD and JPY.
- Yield Curve Implications:
- The shape of the yield curve (the difference between short-term and long-term bond yields) also provides insights into market expectations. A steepening yield curve, where long-term yields rise faster than short-term yields, signals expectations of future economic growth and inflation, potentially boosting the currency. A flattening or inverted yield curve, where short-term yields are higher than long-term yields, can indicate recession fears, often leading to a stronger demand for safe-haven currencies.
C. Examples of Bond Yields Influencing Forex Prices
To illustrate the impact of bond yields on forex prices, let’s consider a few historical examples:
The 2013 Taper Tantrum:
In 2013, when the Federal Reserve announced plans to taper its bond-buying program, U.S. Treasury yields surged as investors anticipated higher interest rates. The rise in yields led to a significant appreciation of the USD against other currencies, particularly emerging market currencies, as investors sought the safety of the U.S. dollar.

COVID-19 Pandemic (2020):
During the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a flight to safety as investors sought U.S. Treasuries, driving yields to historic lows. The USD initially surged as a safe-haven currency, despite falling yields, reflecting the strong demand for safe assets during market turmoil.
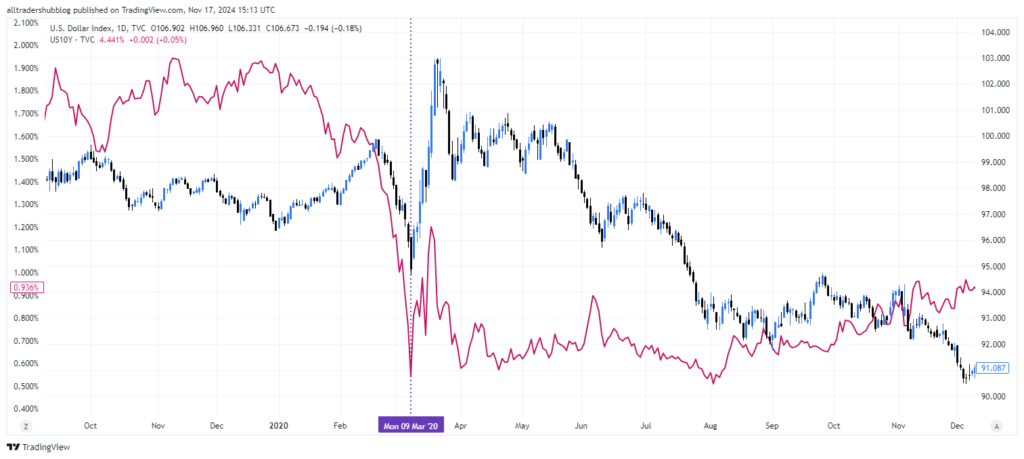
European Central Bank (ECB) Policy Decisions:
When the ECB implemented negative interest rates and large-scale quantitative easing (QE) programs, German Bund yields dropped significantly. This lower yield environment led to a weaker euro, as investors sought higher yields in other markets, strengthening currencies like the USD and GBP against the EUR.

How to Use Bond Yield Analysis in Forex Trading
Integrating bond yield analysis into your forex trading strategy can provide valuable insights and help you anticipate market movements driven by changes in interest rates, economic outlooks, and investor sentiment. Understanding how to interpret bond yields and apply this knowledge to currency trading is a powerful skill for any fundamental analyst.
A. Monitoring Key Bond Yields
One of the first steps in utilizing bond yield analysis is to regularly monitor key bond yields from major economies. Here’s how you can incorporate this into your analysis:
- Focus on Major Economies:
- Keep an eye on government bond yields from major currencies, such as U.S. Treasury yields, German Bund yields, and Japanese Government Bond (JGB) yields. These are crucial indicators because they reflect the market’s expectations about the economic outlook and central bank policies of the respective countries.
- For instance, the U.S. 10-year Treasury yield is closely watched as a barometer of U.S. economic health and interest rate expectations. Significant movements in this yield often trigger reactions in the forex market, influencing the USD’s strength.
- Monitor Yield Differentials:
- Yield differentials, the difference in yields between two countries’ bonds (e.g., U.S. 10-year Treasury yield vs. German 10-year Bund yield), are a critical indicator for forex traders. A widening yield differential typically signals a stronger currency for the country with higher yields, as it suggests better returns for investors.
- For example, if U.S. yields rise relative to Japanese yields, this differential often leads to a stronger USD/JPY pair, as investors shift their capital into U.S. assets to capture higher returns.
- Tracking Short-Term vs. Long-Term Yields:
- Pay attention to both short-term (e.g., 2-year yields) and long-term (e.g., 10-year yields) bonds. The difference between these yields, known as the yield curve, can provide insights into market expectations about future economic growth and central bank actions. A steep yield curve suggests optimism about future growth, while a flat or inverted curve may indicate concerns about an economic slowdown.
B. Analyzing Central Bank Policies Through Bond Yields
Bond yields are directly influenced by central bank policies, making them an essential tool for anticipating changes in interest rates. Here’s how you can use yield analysis to gauge central bank intentions:
- Anticipate Interest Rate Decisions:
- Rising bond yields often indicate that the market expects the central bank to increase interest rates. For instance, if U.S. Treasury yields start climbing, it could be a signal that the Federal Reserve is likely to adopt a more hawkish stance. Forex traders can use this insight to position themselves for a potential appreciation in the USD.
- Conversely, falling bond yields may suggest expectations of rate cuts, signaling potential weakness in the associated currency.
- Monitor Central Bank Communications:
- Central banks regularly provide guidance on their monetary policy outlook through speeches, meeting minutes, and reports. Pay attention to these communications and watch how bond yields react. If the central bank hints at tightening monetary policy (raising rates), bond yields typically rise, which could strengthen the currency.
- Quantitative Easing (QE) and Its Impact:
- During periods of economic weakness, central banks may implement quantitative easing (QE) programs, purchasing large amounts of government bonds to lower yields and stimulate the economy. This can lead to currency depreciation as lower yields make the currency less attractive to investors. Understanding the implications of QE programs can help traders anticipate shifts in currency valuations.
C. Incorporating Yield Analysis Into Your Forex Strategy
To effectively use bond yield analysis in your trading, consider integrating it with other elements of your fundamental and technical analysis toolkit. Here are practical strategies to consider:
- Trading Based on Yield Differentials:
- If you notice a widening yield differential between two countries (e.g., U.S. yields rising faster than Eurozone yields), you might look for opportunities to buy the currency with the higher yield and sell the one with the lower yield. This strategy, known as carry trading, capitalizes on the expected appreciation of the higher-yielding currency.
- Identifying Reversal Signals with Bond Yields:
- Sharp movements in bond yields can signal potential reversals in currency trends. For example, if a currency pair like USD/JPY has been in a downtrend, but U.S. Treasury yields suddenly spike higher, it could indicate a reversal in the pair’s trend as expectations of higher U.S. rates attract investors back to the dollar.
- Using Economic Calendars for Bond-Related Events:
- Track key economic events and releases that can impact bond yields, such as inflation data (CPI), GDP reports, and central bank meetings. Anticipating how these data releases might affect yields can help you position your trades accordingly. For instance, a higher-than-expected inflation report could push bond yields up, signaling potential strength in the related currency.
D. Application of Bond Yield Analysis
To illustrate how traders can use bond yield analysis effectively, let’s look at a few practical scenarios:
- Reacting to an Unexpected Interest Rate Hike:
- Suppose the Bank of England unexpectedly raises interest rates due to surging inflation, causing UK gilt yields to spike. Traders who understand the correlation between bond yields and currency prices might quickly buy the British pound (GBP), anticipating an appreciation against other currencies like the EUR or USD.
- Monitoring U.S. Treasury Yields for USD Strength:
- If U.S. Treasury yields are rising due to expectations of future Federal Reserve rate hikes, traders might look to buy the USD against lower-yielding currencies such as the euro or the Japanese yen. This strategy is based on the expectation that higher U.S. yields will attract more capital flows into U.S. assets, strengthening the dollar.
- Trading Based on ECB’s Bond-Buying Programs:
- When the European Central Bank announces an extension of its bond-buying program (QE), German Bund yields may decline due to increased bond demand. In this scenario, traders might anticipate a weaker euro and position themselves accordingly by shorting EUR/USD.
Limitations and Risks of Using Bond Yield Analysis in Forex Trading
While bond yield analysis is a powerful tool for forecasting forex market movements, it is not without its limitations and potential risks. Relying solely on bond yields to predict currency trends can lead to incomplete or misleading conclusions, especially when other significant factors come into play.
A. The Influence of Other Fundamental Factors
Bond yields are just one of many factors that influence currency prices. Focusing exclusively on bond yields can lead traders to overlook other crucial economic indicators that drive the forex market. Here are some additional factors to consider:
- Geopolitical Events:
- Geopolitical developments, such as trade disputes, elections, and international conflicts, can significantly impact currency prices, often overshadowing the influence of bond yields. For example, during periods of geopolitical tension, investors may flock to safe-haven currencies like the USD or JPY, regardless of changes in bond yields.
- Monetary Policy Expectations Beyond Yields:
- Central bank decisions are not always reflected directly in bond yields. Central banks may use unconventional monetary policy tools, such as negative interest rates or forward guidance, that do not immediately influence bond yields but can have a profound impact on currency values.
- For instance, if the Federal Reserve signals a dovish outlook despite stable bond yields, the USD might weaken as traders anticipate lower future interest rates.
- Economic Data Releases:
- High-impact economic data, such as employment reports (e.g., U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls), inflation data, and GDP figures, can cause significant volatility in the forex market. These releases can lead to abrupt shifts in currency prices that are not directly tied to bond yield movements.
B. Market Sentiment and Risk Appetite
The forex market is heavily influenced by shifts in investor sentiment and risk appetite, which can sometimes cause currency movements that are inconsistent with bond yield trends. Here’s why this can be a challenge:
- Risk-On vs. Risk-Off Dynamics:
- In a risk-off environment, where investors are fearful of economic downturns or geopolitical risks, they often seek safe-haven assets like government bonds and currencies such as the USD or CHF. This can lead to a scenario where bond yields fall due to increased demand for bonds, yet the safe-haven currency strengthens, seemingly contradicting the expected yield-currency correlation.
- Market Overreactions and Herd Mentality:
- Financial markets are prone to overreactions and herd behavior, where investors collectively move in a certain direction based on market sentiment rather than fundamentals. This can lead to temporary distortions in the yield-forex relationship, making it challenging for traders relying on bond yields to predict currency movements accurately.
- Impact of Central Bank Interventions:
- Central banks frequently intervene in bond markets through activities such as quantitative easing (QE) or direct bond purchases. These interventions can artificially suppress or boost bond yields, distorting the natural relationship between yields and currency values. Traders need to be aware of ongoing central bank policies and consider their impact when analyzing bond yields.
C. The Complexity of Interpreting Yield Curves
While the shape of the yield curve can provide valuable insights into market expectations, interpreting it correctly is not always straightforward. The yield curve can flatten, steepen, or invert due to various factors, and each configuration has different implications for the forex market:
- Inverted Yield Curve:
- An inverted yield curve, where short-term yields are higher than long-term yields, is often seen as a recession signal. However, the impact on currency prices can vary depending on the broader economic context. For example, during periods of global economic uncertainty, an inverted U.S. yield curve might lead to a stronger USD as investors seek safe-haven assets.
- Steepening Yield Curve:
- A steepening yield curve typically signals expectations of higher future growth and inflation. However, if the steepening is due to a sharp rise in long-term yields driven by inflation fears, it may lead to currency depreciation, as investors worry about the central bank losing control of inflation.
- Flattening Yield Curve:
- A flattening yield curve, where the difference between short- and long-term yields narrows, can indicate slowing economic growth. While this might suggest a weaker currency due to lower future interest rates, the actual impact depends on the central bank’s response and the market’s interpretation of the economic outlook.
D. Overreliance on Bond Yields and Lack of Diversification
One of the biggest risks in using bond yield analysis is overreliance on this single indicator. Traders who focus exclusively on bond yields may miss other critical signals that could impact their trades. Here’s why a more diversified approach is necessary:
- Ignoring Technical Analysis:
- While fundamental analysis provides the “why” behind market movements, technical analysis offers insights into the “when.” By ignoring technical analysis, traders may fail to identify optimal entry and exit points, leading to suboptimal trading decisions. Combining bond yield analysis with technical indicators, such as support and resistance levels or moving averages, can enhance decision-making.
- Neglecting Other Fundamental Indicators:
- Focusing solely on bond yields without considering other fundamental indicators, such as inflation data, employment figures, or trade balances, can result in an incomplete analysis. For example, a country might have rising bond yields due to inflation expectations, but if the inflation is caused by supply chain disruptions rather than strong economic growth, the currency might not appreciate as expected.
- Overestimating the Predictive Power of Yields:
- While changes in bond yields are a useful indicator, they are not a guaranteed predictor of future currency movements. The forex market is influenced by a multitude of factors, and even significant yield changes might not always translate to expected currency trends due to intervening economic or political developments.
E. Mitigating the Risks of Bond Yield Analysis
To effectively use bond yield analysis while mitigating its risks, traders should adopt a comprehensive approach:
- Combine Fundamental and Technical Analysis:
- Use bond yield analysis in conjunction with other forms of analysis, such as technical indicators and market sentiment analysis, to form a well-rounded view of potential currency movements.
- Stay Informed on Central Bank Policies:
- Keep abreast of central bank statements, meeting minutes, and policy changes, as these can significantly impact bond yields and currency values. Understanding the central bank’s policy stance can help traders anticipate shifts in bond yields and prepare for corresponding currency movements.
- Diversify Your Analysis:
- Consider a range of fundamental indicators alongside bond yields, such as GDP growth rates, inflation data, and geopolitical developments, to build a more comprehensive analysis. This holistic approach can help traders make more informed decisions and reduce the risk of relying on a single indicator.
- Use Risk Management Strategies:
- Implement proper risk management techniques, such as stop-loss orders and position sizing, to protect against unexpected market movements that may not align with bond yield signals. This helps limit potential losses and safeguard your trading capital.
Conclusion
The relationship between bond yields and forex prices is a critical aspect of fundamental analysis in currency trading. Understanding this correlation provides traders with valuable insights into market expectations regarding economic performance, central bank policies, and overall investor sentiment. By effectively integrating bond yield analysis into your forex trading strategy, you can enhance your ability to predict currency movements and make more informed trading decisions. However, mastering this approach requires a comprehensive understanding of its dynamics and limitations.
