Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the process of buying and selling currencies in the global marketplace. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $7 trillion.
Unlike traditional stock markets, Forex operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, making it accessible to traders worldwide. Whether you’re a beginner looking to understand Forex or an investor seeking new opportunities, this lesson will walk you through the basics of Forex trading.
Understanding Forex Trading
The Forex market is different from other financial markets, because it always involves trading currencies as pairs and not as single assets. This means that when you decide to buy a currency, you have to exchange it for another, such as EUR/USD, where the euro is exchanged for the US dollar.
The goal of trading Forex is to profit from changes in the relative value of these currencies as they fluctuate.
-The Concept of Currency Pairs
Currencies are always quoted in pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen). Each pair consists of:
- The Base Currency: The first currency in the pair (e.g., EUR in EUR/USD). This is the currency you are buying or selling.
- The Quote Currency: The second currency in the pair (e.g., USD in EUR/USD). This is the currency used to determine the value of the base currency.
For example, if EUR/USD = 1.1000, it means 1 euro is worth 1.10 US dollars.
-Buying and Selling in Forex
When you place a trade in the Forex market, you are simultaneously:
- Buying the base currency and
- Selling the quote currency
If you believe the euro will rise in value against the US dollar, you would buy EUR/USD (going long). This means you are buying euros while selling an equivalent amount of US dollars.
If you believe the euro will weaken against the US dollar, you would sell EUR/USD (going short). This means you are selling euros while buying US dollars.
-Profiting from Exchange Rate Movements
As we said earlier, the end goal of trading Forex is to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. Here’s an example:
- Suppose you buy EUR/USD at 1.1000 (buying euros, selling dollars).
- Later, the exchange rate rises to 1.1200 (meaning the euro has strengthened against the dollar).
- You then sell your euros at this new price. Since you initially bought at 1.1000 and sold at 1.1200, you made a 200-pip profit.
Conversely, if the exchange rate had dropped to 1.0800, you would have incurred a loss if you sold at that point.
Key Aspects of Forex Trading
-Decentralized Market
Unlike stock markets that operate through centralized exchanges, Forex trading takes place over the counter (OTC). This means transactions occur directly between participants via electronic networks and brokerages, allowing for more flexibility and continuous trading.
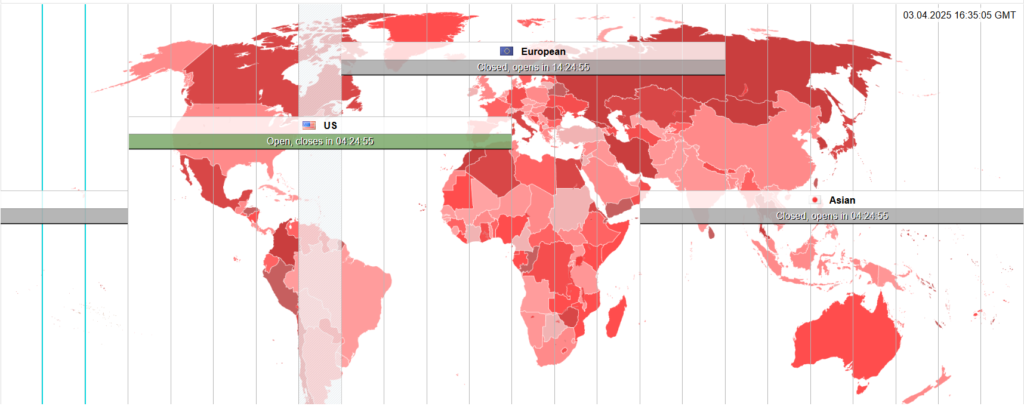
-Market Hours
Unlike the stock market, the Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, due to the global nature of currency trading. The trading day starts with the Asian markets on Monday and ends after the New York session on Friday. The major trading sessions include:
- Asian Session (Tokyo)
- European Session (London)
- North American Session (New York)
-Currency Pairs
Currencies are traded in pairs, categorized into three groups:
- Major Pairs:
These currency pairs are the most traded pairs in the Forex market and always include the US dollar (USD). These pairs have high liquidity, lower spreads, and less volatility compared to other pairs. For example: EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF.
- Minor Pairs:
These are currency pairs that do not include the US dollar. These pairs usually have lower liquidity and slightly wider spreads compared to major pairs. For example: EUR/GBP, AUD/NZD, CAD/JPY.
- Exotic Pairs:
The exotic pairs involve one major currency paired with a currency from an emerging or smaller economy. These pairs tend to have lower liquidity, wider spreads, and higher volatility, making them riskier to trade. For example: USD/TRY, EUR/SGD, GBP/ZAR.
-Leverage and Margin
Margin and leverage are two important parameters in Forex trading. Leverage allows traders to control a large position with a small investment. For example, a leverage ratio of 100:1 means a trader can control $100,000 with just $1,000. While leverage amplifies potential profits, it also increases the risk of losses.
Margin involves borrowing money from a brokerage firm to purchase securities. This borrowed amount is secured by the value of the assets in your account, such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds.
-Liquidity and Volatility
Forex is known for its high liquidity, meaning traders can enter and exit positions quickly. However, volatility varies depending on economic events, central bank decisions, and global news, which can lead to rapid price fluctuations.
How Forex Trading Works
Forex trading involves executing buy or sell orders based on market conditions. Here’s an example:
- If a trader believes the euro will strengthen against the US dollar, they will buy EUR/USD.
- If the euro appreciates, they can sell it at a higher price for a profit.
- If the euro depreciates, they incur a loss.
As you become more familiar with trading, you will hear the term Pip a lot, as price movements are measured in pips (percentage in points). Pips are generally speaking representing the smallest price change in a currency pair.
Forex Trading Strategies
Every trader in the Forex market has to have a well-designed and back-tested strategy. A strategy is simply a set of rules that you follow in order to decide whether you buy or sell a currency pair, and also where to enter and exit a position. There are several strategies that traders use to maximize profits and minimize risks:
-Trend Trading
Traders identify the market trend (upward or downward) and trade in its direction. This involves technical indicators like moving averages and trendlines.
-Range Trading
This strategy involves identifying support and resistance levels where prices fluctuate within a range. Traders buy at support and sell at resistance.
-Breakout Trading
Traders watch for price movements beyond key support or resistance levels, anticipating a strong move in that direction.
Benefits and Risks of Forex Trading
-Benefits
- High Liquidity: The vast number of participants ensures smooth trading with minimal price manipulation.
- 24-Hour Market: Allows for flexibility in trading schedules.
- Leverage Opportunities: Traders can control large positions with small capital.
- Profit Potential: Traders can profit in both rising and falling markets.
-Risks
- Market Volatility: Sudden price movements can result in significant losses.
- Leverage Risks: While leverage can amplify gains, it also increases potential losses.
- Lack of Knowledge: Many beginners enter the market without adequate education, leading to poor trading decisions.
Resources for Learning Forex Trading
For beginners, using reputable resources is crucial for learning Forex trading. Some recommended platforms include:
- Plus500: Beginner-friendly guide to Forex trading.
- Saxo Bank: Comprehensive educational materials and trading platforms.
- FOREX.com: Trading academy with tutorials and a demo account.
Additionally, joining Forex trading communities, watching market analysis videos, and practicing with demo accounts are effective ways to gain hands-on experience.
Conclusion
Forex trading presents a unique opportunity for traders to profit from the global currency markets. However, it requires a strong understanding of market mechanics, risk management, and trading strategies.
By using reliable learning resources and practicing disciplined trading, beginners can navigate this complex yet rewarding market.
If you’re new to Forex, start with education, practice on demo accounts, and gradually transition to live trading with a solid strategy.