Monthly Macro Report: United States Economy
The U.S. economy displayed mixed signals in recent macroeconomic data. Key indicators point to slight improvements in consumer confidence and service sector activity but also highlight challenges in manufacturing, nonfarm payrolls, and housing. The Federal Reserve’s decision to lower the interest rate by 25 basis points further underscores growing concerns about economic momentum and inflationary trends.
Key Economic Indicators Analysis
1. Manufacturing Sector: ISM Manufacturing Index
- November PMI: 48.4% (up from 46.5% in October).
- The manufacturing sector contracted for the 8th consecutive month, though the pace of contraction slowed.
- Only the New Orders sub index moved into weak expansion, while the Production Index remained in contraction.
- Of the six largest industries, Food, Beverage & Tobacco Products and Computer & Electronic Products registered growth.
- A PMI above 42.5% indicates overall economic expansion; November’s reading corresponds to an estimated +1.7% annualized GDP growth.
- Future Outlook: Manufacturing may stabilize if demand recovers, but sustained growth hinges on monetary easing and improvements in global economic conditions.
- Forex Impact: The weak ISM reinforces a bearish sentiment on the USD as manufacturing struggles signal broader economic fragility.
2. Service Sector: ISM Non-Manufacturing Index (NMI)
- October PMI: 56% (up from 54.9% in September).
- The services sector continued to expand, reaching its highest level since July 2022.
- The Services PMI indicates overall economic expansion for the 4th straight month.
- October’s reading corresponds to an estimated +2.3% annualized GDP growth.
- Future Outlook: Services are likely to continue driving economic growth, supported by a healthy labor market and resilient consumer activity.
- Forex Impact: A thriving service sector supports a moderate bullish case for the USD against peers with weaker economic conditions.
Key Insight: While manufacturing remains in contraction, services are driving economic growth, supporting overall GDP expansion.
3. Consumer Confidence
- October: 70.5
- November: 71.8
Consumer confidence rose for two consecutive months, suggesting improving household sentiment. This increase aligns with a deceleration in inflation and lower interest rates.
- Future Outlook: Confidence may further improve if inflation remains contained and labor market conditions hold steady.
- Market Sentiment: Higher consumer confidence bolsters risk appetite in equity markets, potentially dampening safe-haven flows into the USD.
4. Housing Market: Building Permits
- August: 1,470k
- September: 1,425k
- October: 1,419k
The housing market remains subdued, with building permits declining slightly over three months. Elevated mortgage rates and affordability challenges continue to constrain housing activity.
- Future Outlook: Further rate cuts could support a modest recovery in housing starts, though the sector faces structural challenges.
- Forex Impact: A sluggish housing market contributes to a dovish USD outlook, reflecting broader economic uncertainties.
5. Money Supply (M2)
- September: $21,223 billion
- October: $21,311 billion
The slight increase in M2 money supply reflects easing liquidity constraints, likely influenced by the Federal Reserve’s accommodative measures.
- Future Outlook: Expanding money supply supports financial stability and credit availability, though excessive growth may reignite inflationary pressures.
- Market Sentiment: An expanding money supply could weaken the USD if perceived as inflationary or reflecting looser monetary conditions.
6. Interest Rates
- October: 5%
- November: 4.75%
The Federal Reserve’s decision to cut rates signals a shift in monetary policy to counteract slowing economic growth. This adjustment aligns with softening inflation and labor market trends.
- Forex Impact: A rate cut typically exerts downward pressure on the USD, especially if other central banks maintain tighter stances.
7. Labor Market
- Nonfarm Payrolls:
- September: +223k
- October: +12k
- Unemployment Rate:
- September: 4.1%
- October: 4.1%
The labor market showed signs of deceleration, with a dramatic decline in NFP growth in October. The unemployment rate remained steady but could rise if job creation continues to falter.
- Future Outlook: Weakening labor market trends may prompt further rate cuts, adding downward pressure on the USD.
- Market Sentiment: A soft labor market fuels risk-off sentiment, benefiting safe-haven assets like gold or the JPY.
8. Inflation
- September: 2.4%
- October: 2.6%
Inflation ticked up slightly in October but remains well within the Federal Reserve’s target range. Higher energy prices could contribute to inflationary risks in the coming months.
- Future Outlook: Inflationary pressures are expected to remain moderate, allowing the Fed more flexibility for additional rate cuts.
- Forex Impact: Stable inflation limits sharp USD movements, though higher inflationary risks could reignite volatility.
9. Treasury Yields
- October: 4.284%
- November: 4.177%
Declining 10-year Treasury yields reflect market anticipation of further monetary easing and slowing economic growth.
- Market Sentiment: Lower yields reduce the attractiveness of USD-denominated assets, weighing on the currency.
10. Central Bank Balance Sheet to GDP
- Q2 2024: 31.97%
- Q3 2024: 30.61%
The shrinking balance sheet signals ongoing quantitative tightening despite rate cuts. This divergence may temper the dovish impact on the USD.
Conclusions and Forex Implications
- USD Outlook:
- Bearish near-term sentiment due to rate cuts, weak manufacturing, and soft labor market data.
- Limited support from the service sector and resilient consumer confidence.
- Market Sentiment:
- Risk appetite may improve with lower rates, benefiting equity markets.
- Continued economic uncertainty supports demand for safe-haven currencies like the JPY and CHF.
- Future Expectations:
- The Federal Reserve’s dovish pivot may continue, with further rate cuts likely if labor and manufacturing weakness persist.
- USD depreciation expected against currencies of economies with stronger growth or higher rates, such as the EUR or GBP.
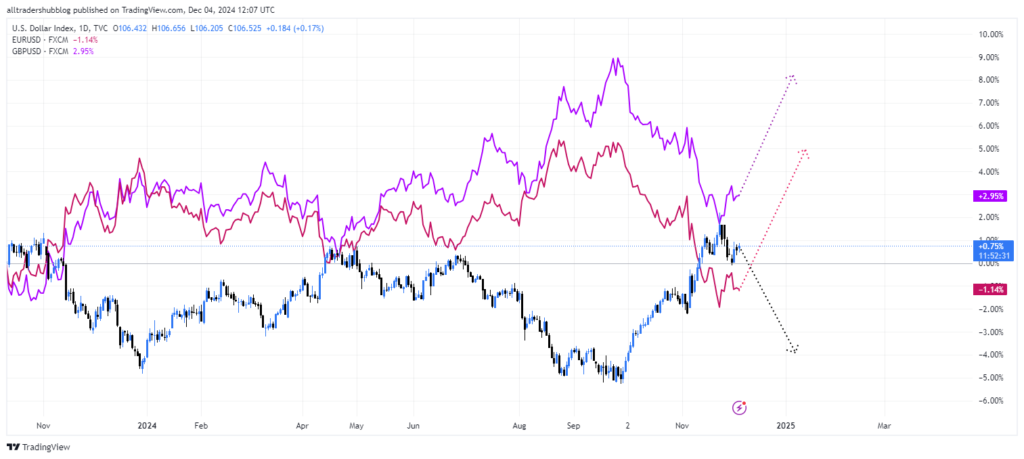
This report outlines a nuanced economic landscape, with significant implications for forex traders navigating shifting monetary policies and market sentiment.
